a. What is the kinetic energy of the protons when they are ejected from the cyclotron? KE at ejection = b. What is this energy in MeV? KE at ejection in MeV = MeV c. Through what total potential difference (potential difference between the gaps and number of trips through the gaps) would a proton have to be accelerated to acquire this kinetic energy? Think about the magnitude of potential you have calculated. While designing the cyclotron, gap potential can be made much smaller than this magnitude by making the proton pass through the gap several times by making it pass through a magnetic field and confining the protons to a circular path before the next increment in energy. Potential difference = MV d. What is the period of the voltage source used to accelerate the protons? Hint: For maximum energy transfer from the external voltage source to the proton, the period of the oscillating voltage should coincide with the period of oscillation of the proton. Period of the voltage source = S
a. What is the kinetic energy of the protons when they are ejected from the cyclotron? KE at ejection = b. What is this energy in MeV? KE at ejection in MeV = MeV c. Through what total potential difference (potential difference between the gaps and number of trips through the gaps) would a proton have to be accelerated to acquire this kinetic energy? Think about the magnitude of potential you have calculated. While designing the cyclotron, gap potential can be made much smaller than this magnitude by making the proton pass through the gap several times by making it pass through a magnetic field and confining the protons to a circular path before the next increment in energy. Potential difference = MV d. What is the period of the voltage source used to accelerate the protons? Hint: For maximum energy transfer from the external voltage source to the proton, the period of the oscillating voltage should coincide with the period of oscillation of the proton. Period of the voltage source = S
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The accleration of protons in a cyclotron is shown in the figure below.
The magnetic field in a cyclotron is 1.25 T, and the maximum orbital radius of the circulating protons
is 0.4 m. The mass of a proton is 1.67·10-27 kg and the charge on a proton is 1.6-10-1⁹ C.
Dee
O
O/O
O
O OI
I
O
10
O
Ion source
O
O
O
O
O
O
Electric oscillator
O
Deflector plate
Target
Electric field region where
kinetic energy is gained
Proton beam

Transcribed Image Text:a. What is the kinetic energy of the protons when they are ejected from the cyclotron?
KE at ejection =
J
b. What is this energy in MeV?
KE at ejection in MeV =
MeV
c. Through what total potential difference (potential difference between the gaps and number of trips
through the gaps) would a proton have to be accelerated to acquire this kinetic energy?
Think about the magnitude of potential you have calculated. While designing the cyclotron, gap
potential can be made much smaller than this magnitude by making the proton pass through the gap
several times by making it pass through a magnetic field and confining the protons to a circular path
before the next increment in energy.
Potential difference =
MV
d. What is the period of the voltage source used to accelerate the protons? Hint: For maximum
energy transfer from the external voltage source to the proton, the period of the oscillating voltage
should coincide with the period of oscillation of the proton.
Period of the voltage source =
✔S
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
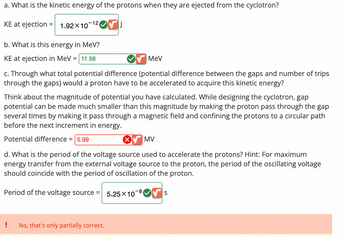
Transcribed Image Text:a. What is the kinetic energy of the protons when they are ejected from the cyclotron?
KE at ejection
= 1.92×10 VI
-12
b. What is this energy in MeV?
KE at ejection in MeV = 11.98
c. Through what total potential difference (potential difference between the gaps and number of trips
through the gaps) would a proton have to be accelerated to acquire this kinetic energy?
Think about the magnitude of potential you have calculated. While designing the cyclotron, gap
potential can be made much smaller than this magnitude by making the proton pass through the gap
several times by making it pass through a magnetic field and confining the protons to a circular path
before the next increment in energy.
Potential difference = 5.99
MV
d. What is the period of the voltage source used to accelerate the protons? Hint: For maximum
energy transfer from the external voltage source to the proton, the period of the oscillating voltage
should coincide with the period of oscillation of the proton.
Period of the voltage source =
No, that's only partially correct.
MeV
X
5.25 X 10
-8
S
Solution