
Concept explainers
This problem concerns the m. o module from Figure 7.5 and the following version of the swap, c function that counts the number of times it has been called:

For each symbol that is defined and referenced in swap. o, indicate if it will have a symbol table entry in the symbol section in module swap. o. If so, indicate the module that defines the symbol (swap .o or m. o), the symbol type (local, global, or extern), and the section (.text, .data, or bss) it occupies in that module.
Sections in relocatable object files:
There are many sections in a relocatable object file. They are given below:
- “.text”:
- It is the machine code of the compiled program.
- “.rodata”:
- This section is used to read only the data in the format such as
- Strings in “printf” statements.
- Jump tables for switch statements.
- This section is used to read only the data in the format such as
- “.data”:
- This section is used in the initialized “C” variables of global variable and static “C” variables.
- Local “C” variables are initialized at execution time on the stack.
- It does not show in either the “.data” or “.bss” sections.
- “.bss”:
- It is used in the uninitialized global and static “C” variables, along with any global or static variables that are assigned to zero.
- “.symtab”:
- It is a symbol table.
- It contains the information about functions and global variables that are defined and referenced in the program.
- “.rel.text”:
- This section contains a list of locations in the “.text” section.
- It will require to be changed once the linker merges this object file with others.
- This section contains a list of locations in the “.text” section.
- “.rel.data”:
- This section contains relocation information for any global variables that are referenced or defined by the module.
- “.debug”:
- It is a symbol table for debugging
- It contains entries for following
- Definition of Local variables, global variables and typedefs variables and original “C” source file.
- “.line”:
- It is a mapping between line numbers in the given program
- That is in original “C” source program and machine code instructions in the “.text” section.
- It is a mapping between line numbers in the given program
- “.strtab”:
- It is a string table.
- It contains symbol tables in the “.symtab” and “.debug” sections.
- It is the table for section names in the section headers.
- It is a string table.
Explanation of Solution
For symbol “buf”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is an “extern” type. Because, the variable “buf” is declared in “extern” type which is present in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “buf” type is defined in “m.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “buf” are defined in “m.c” file”.
- When converting source file “m.c” to a relocatable object file, the given file becomes “m.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “buf” is defined in “.data” section. It is the initialized global variable of “m.c” file.
For symbol “bufp0”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “global” symbol type. Because, the variable “bufp0” is declared outside the function in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “bufp0” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “bufp0” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable object file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “bufp0” is defined in “.data” section. It is the initialized global variable of “swap.c” file
For symbol “bufp1”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “local” type. Because, the variable “bufp1” with “static” type in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “bufp1” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “bufp1” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable object file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “bufp1” is defined in “.bss” section. It is the uninitialized static “C” variable of “swap.c” file
For symbol “swap”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “global” type. Because, the symbol “swap” is used in the entire program.
- Module defined position:
- The “swap” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “swap” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “swap” is present in “.text” section. It is the machine code of the compiled program.
For symbol “temp”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- The local variable “temp” does not a have a symbol table entry.
- So, it does not have a symbol type, module defined position and section.
- The local variable “temp” does not a have a symbol table entry.
For symbol “incr”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “local” type. Because, the function “incr” uses return type of “static” in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “swap” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “swap” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “swap” is present in “.text” section. It is the machine code of the compiled program.
For symbol “count”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “local” type. Because, the variable “count” declared in “static” type in the “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “swap” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “swap” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “swap” is present in “.bss” section. Here, the static variables “count” are initialized to “0” in “swap.c” file.
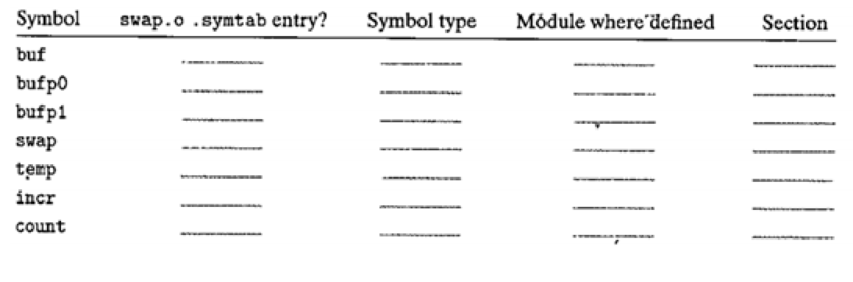
The final table is
| Symbol | .symtab entry? | Symbol type | Module where defined | Section |
| buf | Yes | extern | m.o | .data |
| bufp0 | Yes | global | swap.o | .data |
| bufp1 | Yes | local | swap.o | .bss |
| swap | Yes | global | swap.o | .text |
| temp | No | - | - | - |
| incr | Yes | local | swap.o | .text |
| count | Yes | local | swap.o | .bss |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (3rd Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Concepts of Programming Languages (11th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (3rd Edition)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach
Software Engineering (10th Edition)
- Using c++ oop solve below program.Make function and call them into main function. Add new Shop Keeper To add a new shop keeper, your program should ask some credentials from the user to register a shop keeper. Credentials you must ask includes: S-id (Shop keeper id) should be in proper format as string to use in future modules [All the info should be taken in same order] ⮚ First Name ⮚ Last Name ⮚ S-id (should be auto generated by the system in increasing order) [format should be Shopkeeper e.g., 0001 for first shopkeeper and 1001 for one thousand and one shopkeeper number] ⮚ Username ⮚ Email ⮚ Password ⮚ Registration Date ⮚ Gender ⮚ Blood Group ⮚ Contact No ⮚ Address After this, you must record all the above-mentioned data save data within a file named as “shopkeeper.txt” present in the same directory. \ Edit Shopkeeper details Your program should be capable of editing the shopkeeper's basic details. The details that administrator can edit includes: ⮚…arrow_forwardQ # 1. Note: write in c programming. Implement a Result Compilation System for CP Course. Program will take Marks of 3 Quizzes, 2 assignments, one midterm and one final term from the user as input. Marks of each quiz will be out of 15, marks of each assignment will be out of 40. Marks of Midterm will be out of 60 and Final term out of 80. Program will compute total marks in the subject according to the following grading scheme and display on the screen. 图 Category Weightage 1 Quizzes 25% 2 Assignments 15% 3 Mid-term 20% 4 Final-term 40% Total Marks 100arrow_forwardThe memory diagram contains (i) and several pointers. Write a code to declare i, x, y, z and w with the correct types and set their values so they align with the diagram.arrow_forward
- In C Language, take an infix expression from the user and write a program to check the bracket evaluation of the expression. Do not user pointers and make your code as efficient as possible.arrow_forwardIn C++ Language using OOP, take an infix expression from user and convert to postfix and then evaluate. Do not use pointers and make sure the program is efficient and simple. Please do not copy from the internet.arrow_forwardUsing a pointer as the return value is considered a poor practise in C. For example, how does dynamic memory allow us to return an object pointer from a function safely?arrow_forward
- Write these codes in c language please. Thank you in advance. 1. Add two more statements to main() to test inputs 3 and -1. Use print statements similar to the existing one (don't use assert). 2. Using the CelsiusToKelvin function as a guide, create a new function, changing the name to KelvinToCelsius, and modifying the function accordingly. 3. Write a function SwapArrayEnds() that swaps the first and last elements of the function's array parameter. Ex: sortArray = {10, 20, 30, 40} becomes {40, 20, 30, 10}.arrow_forwardWhat is the method for storing local declarations in computer memory? Is there any reason to avoid using local declarations if the same objective can be achieved without them? Why use value parameters if reference parameters can be used in any function? What role do value parameters play in program data processing?arrow_forwardIn C language please; Requirements: You must use the correct program and function descriptions. You must use a user defined function for the sequential search and it must use pointers to keep track of the number of successful searches as well as how many test comparisons were made. You must use the srand() function and offset and range correctly.arrow_forward
- 3. Implement the following function in the PyDev module functions.py and test it from a PyDev module named t03.py: 1 def get digit_name(n): 4 6 7 9 10 11 12 Returns the name of a digit given its number. Use: name get digit_name(n) Parameters: 'tuo' n digit number (int 8arrow_forwardTask using C language One common way of verifying if the data integrity of a file was preserved during a copy or transmission is to verify if the checksum matches. The checksum is a small piece of data computed from the original data. Your task is to compute a recursive function that maps an integer into a single digit to be used as checksum. Given an input integer in the range from 0 to 1012, the checksum is the sum of the digits of the input number. While the resulting sum has multiple digits, the checksum will be the sum of its digits instead. For instance: if the input is 34, the checksum is 7 (3+4); if the input is 99, the sum of its digits is 18 (9+9), so the checksum is 9 (1+8); if the input is 99999999999, the sum of its digits is 99 (9+9+9+9+9+9+9+9+9+9+9), whose sum of digits is 18 (9+9), so the checksum is 9 (1+8). Requirements Follow the format of the examples below. Make sure your variables and parameters have the correct data types. You must implement a recursive…arrow_forwardExplain the concept of pass by reference. How it differs from pass by valuearrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





