
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The Lewis diagram for
Concept introduction:
The Lewis structure shows the connectivity between atoms by identifying the lone pairs of electrons in a compound. Lewis structures are also known as Lewis dot structures. The valence electrons around an atom are shown by dots. Bonds between atoms are shown by lines and the lone pair of electrons is shown by a pair of dots.
Answer to Problem 10E
The Lewis diagram for
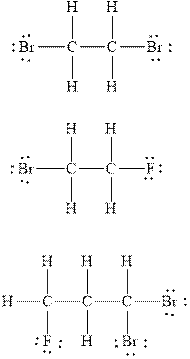
Explanation of Solution
The number of valence electrons in the carbon atom is
In
Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in
These valence electrons are distributed in the Lewis diagram using bonds and lone pair of electrons.
At first, the single bond between the carbon atoms surrounded by other atoms through single bonds is drawn. Each bond contains
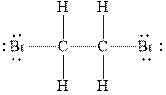
Figure 1
In
Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in
These valence electrons are distributed in the Lewis diagram using bonds and lone pair of electrons.
At first, the single bond between the carbon atoms surrounded by other atoms through single bonds is drawn. Each bond contains
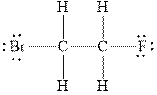
Figure 2
In
Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in
These valence electrons are distributed in the Lewis diagram using bonds and lone pair of electrons.
At first, the single bond between the carbon atoms surrounded by other atoms through single bonds is drawn. Each bond contains
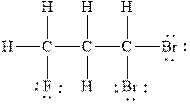
Figure 3
The Lewis diagram for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
- Successive substitution of F atoms for H atoms in the molecule NH3 produces the molecules NH2F, NHF2, and NF3. a. Draw Lewis structures for each of the four molecules. b. Using VSEPR theory, predict the geometry of each of the four molecules. c. Specify the polarity (polar or nonpolar) for each of the four molecules.arrow_forwardUsing the symbols and +, indicate the direction of polarity in each polar covalent bond. (a) CN (b) NO (c) CClarrow_forwardSuccessive substitution of F atoms for H atoms in the molecule CH4 produces the molecules CH3F, CH2F2, CHF3, and CF4. a. Draw Lewis structures for each of the five molecules. b. Using VSEPR theory, predict the geometry of each of the five molecules. c. Specify the polarity (polar or nonpolar) for each of the five molecules.arrow_forward
- Draw the Lewis structure of these compounds and use the electronegativity values, calculate the polarity of the molecules and write if the compounds will be polar, nonpolar, or ionic. Label the + and -next to the atoms of the molecule if they have charge. Also, write the overall dipole. CH₄ O₂ CH₂Cl₂ H₂O CH₃Liarrow_forwardWrite a Lewis structure for each of the following simple molecules. Show all bonding valence electron pairs as lines and all nonbonding valence electron pairs as dots. NBr3 HF CBr4 C2H2arrow_forwardFor the structure CIO3 draw a Lewis structure using Cl as the central atom... For the structure that obeys the octet rule which of the following are correct? There are a total of 26 valence electrons There are a total of 24 valence electrons There are a total of 25 valence electrons OCI has one lone pair of electrons CI makes a double bond to one of the oxygens Each O has a -1 formal charge 20 atoms make a double bond to Cl All 30 atoms make a double bond to Clarrow_forward
- 1) Draw the Lewis symbol for each element in the compounds below, then draw a Lewis Structure for the compounds. PH3 SiF4 H2O O2arrow_forwardDraw out the Lewis structures and using VSEPR THEORY determine which of the following species have the same shape NC13 PF3 A1C13 CO3^-2arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure of these compounds and use the electronegativity values, calculate the polarity of the molecules and write if the compounds will be polar, nonpolar, or ionic. Label the + and -next to the atoms of the molecule if they have charge. Also, write the overall dipole. Cl₂ HCl NH₃ CH₂Oarrow_forward
- Draw a Lewis structure for the compound whose skeletal structure is provided to you below. Don't forget to draw in the H atoms! CH₂ HC CH 11 HC — CH, - Draw the Lewis structure by placing atoms on the grid and connecting them with bonds. Include all lone pairs of electrons.arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure of these compounds and use the electronegativity values, calculate the polarity of the molecules and write if the compounds will be polar, nonpolar, or ionic. Label the + and -next to the atoms of the molecule if they have charge. Also, write the overall dipole. Cl₂ HCl NH₃ CH₂O CH₄ O₂ CH₂Cl₂ H₂O CH₃Li HCN CH₂CHCl CH₃CH₃ CO₂arrow_forwardPredict the molecular structure, bond angles, and polarity (dipole moment) for each of the following. Formula Molecular structure Bond angles Dipole moment XeF4 KrCl4 BH3 IF3 NH4* BrF3 > > > > >arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


