
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To write the structural formula of the lowest molecular weight chiral molecule of
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
- A plane of symmetry
- A centre of symmetry
- n-fold alternating axis of symmetry.
Answer to Problem 15.18P
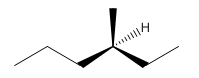
Explanation of Solution
Since alkanes consist of only carbon and hydrogen, the lowest molecular weight alkane can have four different groups attached to it namely- hydrogen, methyl group, ethyl group, and propyl group.
So the molecule so formed is: 3-Methyl-Hexane.
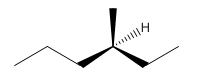
3-Methyl-Hexane.
(b)
Interpretation:
To write the structural formula of the lowest molecular weight chiral molecule of
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
- A plane of symmetry
- A centre of symmetry
- n-fold alternating axis of symmetry.
Answer to Problem 15.18P
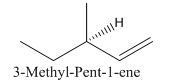
Explanation of Solution
Since alkenes consist of only carbon and hydrogen, with a double bond, the lowest molecular weight alkene can have four different groups attached to it namely- hydrogen, methyl group, vinyl group, and ethyl group.
So the molecule so formed is: 3-Methyl-Pent-1-ene.
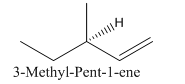
(c)
Interpretation:
To write the structural formula of the lowest molecular weight chiral molecule of alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
- A plane of symmetry
- A centre of symmetry
- n-fold alternating axis of symmetry.
Answer to Problem 15.18P
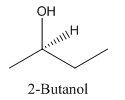
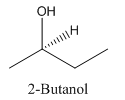
Explanation of Solution
Since alcohol consist of carbon and hydrogen and oxygen, the lowest molecular weight alcohol can have four different groups attached to it namely- hydrogen, methyl group, hydroxyl group, and ethyl group.
So, the molecule so formed is: 2-Butanol.
(d)
Interpretation:
To write the structural formula of the lowest molecular weight chiral molecule of alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
- A plane of symmetry
- A centre of symmetry
- n-fold alternating axis of symmetry.
Answer to Problem 15.18P
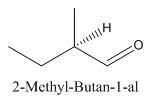
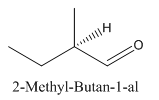
Explanation of Solution
Since
So the molecule so formed is: 2-Methyl-Butan-1-al.
(e)
Interpretation:
To write the structural formula of the lowest molecular weight chiral molecule of alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
- A plane of symmetry
- A centre of symmetry
- n-fold alternating axis of symmetry.
Answer to Problem 15.18P
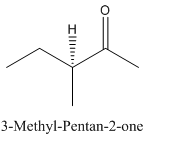
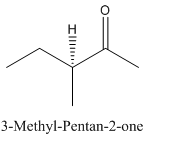
Explanation of Solution
Since
So, the molecule so formed is: 3-Methyl-Pentan-2-one.
(f)
Interpretation:
To write the structural formula of the lowest molecular weight chiral molecule of alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
- A plane of symmetry
- A centre of symmetry
- n-fold alternating axis of symmetry.
Answer to Problem 15.18P
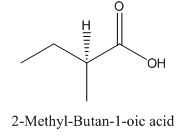
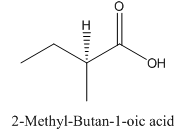
Explanation of Solution
Since
So, the molecule so formed is: 2-Methyl-Butan-1-oic acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- OH 1. Consider this compound: CH;CH2CHCH,CHCH2CH3 ČH3 a) How many chiral carbons does this compound have? b) What is the maximum number of stereoisomers that could exist for this compound? Show how you arrived at your answer.arrow_forwardPart 1 of 2 Each of the following compounds can exhibit optical activity. Enter the label number of chiral center(s) in the following compounds. If more than one, separate them with commas. H OF || | | HO-C-C-C=C-H 121 H 3 The chiral center(s) is/are at Part 2 of 2 H-C-H H Garrow_forwardUsing only C, H, and O, write structural formulas for the lowest-molecular-weight chiral. Q) Alkanearrow_forward
- Assign the absolute configuration of the chiral carbon in Compound Q below. Compound Q OH b) When Q is treated with an oxidizing agent, it forms Compound P. (The alcohol is oxidized to a carboxylic acid.) Assign the absolute configuration of the chiral carbon in Compound P. OH oxidation OH c) If you did a) and b) correctly, the chiral carbon should have changed its absolute configuration even though it was not involved in the reaction Explain what happens.arrow_forward17-74 Glucose, C6H12O6, contains an aldehyde group but exists predominantly in the form of the cyclic hemiacetal shown here. We will discuss this cyclic form of glucose in Chapter 20. A cyclic hemiacetal is formed when the —OH group of one carbon bonds to the carbonyl group of another carbon. (a) Which carbon in glucose provides the —OH group and which provides the —CHO group? (b) Draw the alternative chair confirmations of D-glucose and state which of the two is the more stable.arrow_forwardWhat functional groups are present in: m-nitroanline? n,n-dimethyl aniline? cholesterol? palmitic acid? napthalene? Please list all. I have 2 benzene groups for napthalene. Palmitic Acid: 15-carbon alkane and carboxylic group N,N-dimethyl aniline:amine and phenol Cholesterol: alcohol and alkene M-nitroaniline; amide but not sure what else. Please help. Thank you.arrow_forward
- - entel® ZEH10 Ⓡ raser de haute qualité de calidad superior CHO AP S a) Assign the absolute configuration of the chiral carbon in Compound Q below. Br Compound Q OH b) When Q is treated with an oxidizing agent, it forms Compound P. (The alcohol is oxidized to a carboxylic acid.) Assign the absolute configuration of the chiral carbon in Compound P. Br OH oxidation Br OH c) If you did a) and b) correctly, the chiral carbon should have changed its absolute configuration even though it was not involved in the reaction. Explain what happens.arrow_forwardCortisone is a compound that is used as an anti-inflammatory drug to treat 2) diseases like arthritis. Cortisone is a steroid which contains four rings (A, B, C and D), and has the following structure: он "OH Cortisone Provide the data to complete each of the following statements: The total number of chiral carbons (stereocentres) in Cortisone is The maximum number of stereoisomers possible is: The degree of unsaturation (IHD) of Cortisone is The total number of 2° hydrogens is The ring fusion between rings B and C is trans or cis? The absolute configuration of the carbon with * in the structure is The total number of n bonds isarrow_forwardnt Answer true or false. (a) The functional group of an alcohol is the -OH (hydroxyl) group. 1 (b) The parent name of an alcohol is the name of the longest carbon chain that contains the -OH group. (c) 1°, 2°, and 3° refer to the number of carbon groups bonded to the carbon bearing the -OH group. (d) In the IUPAC system, the presence of three -OH groups is shown by the ending -triol. (e) Glycols are diols where the two hydroxyl groups are bonded to two adjacent carbons. (f) Because of the presence of an -OH group, all alcohols are polar compounds. (g) The boiling points of alcohols decrease with increasing molecular weight. Q $ 0 % [References] L MacBook Pro Cengage Learning Cengage Technical Support Œ (arrow_forward
- FO 23: Identify and draw conformers. NH₂ NH2 NH2 NH2 NH2 NH2 1 NH2 NH2 4 2 3 (a) List any two structures that are related as conformers. Answer by listing exactly two numbers. (b) Draw one conformer of the new structure shown here: 1 and 3 (b) OH HO OHarrow_forward1. How many chiral carbon atoms are in the following compound? CHCIBRCH2CHBRCH3 a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3 4. Which of the following compounds will not show optical activity? a) CH2CICHBRCI b) CH;CH(OH)CH3 c) CH;CH2CHĆICH3 d) CH2(OH)CH(NH2)COOH 2. How many chiral carbon atoms are in the following compound? 5. Three of the following projection formulas are the same compound. The other is the enantiomer. Which is the enantiomer? CH2(OH)CH(OH)CH(OH)CH(OH)CH2OH CH,OH c=0 a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 ОН Н H-C=0 a) НО -H 3. The maximum number of ČHHOH stereoisomers theoretically possible for the compound below is: b) H-C =0 -CH2OH CH2(OH)CH(OH)CH(OH)CH(OH)CHO c) CH2OH a) 8 b) 6 c) 16 d) 4 H. - OH d) H-C=0arrow_forward22 pts Question 3 For each chiral carbon labeled in the structures below (see the numbers), assign R or S absolute configuration in the boxes provided - you only need to enter R or S. Then, state (in the box provided) whether the molecules are enantiomers, identical, diastereomers, or not related. O Br CH3 and a. 2 C1- C3- b. C1- C. 1 Me Br 1 Me OH 1 O OH C2- C4- and C2- and Et 3 2 CH3 Et 4 OH Related- Related- MacBook Proarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

