
Concept explainers
The objective function and the constraint equations for minimizing the transportation cost for the community.
Answer to Problem 3.16P
The objective function for minimizing the transportation cost for the community is
The constraint equations are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The community is shown in the figure below:
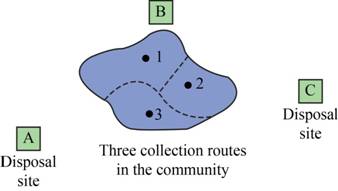
Figure (1)
Assume that the cost of disposal is the same at both the disposal sites, and therefore, the disposal cost can be ignored.
Write the expression for the general objective equation for transportation cost.
Here, the transportation cost is
In Figure-(1) there are three routes, this means there are three sources and two disposal sites A and B.
Substitute
From the given data disposal cost can be ignored.
Thus, expand the above equation to find the transportation cost.
Write the
The waste hauled is equal to or less than the capacity of the disposal sites.
Here, the disposal site is
Expand Equation (II) to find the
Write the
The waste hauled is equal to the capacity of the disposal sites.
Here, the disposal site is
Expand Equation (III) to find the
The quantity of the waste hauled out must be positive.
Conclusion:
Thus, the objective function for minimizing the transportation cost for the community is
The constraint equations are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Define the following terms (Answer only five) 1. Mass balance equation 2. Detention storage 3. Mass curve 4. Unit hydrograph 5. Ground water depletion curve 6. Percolation 7. Ø-indexarrow_forwardConsider the following project network. Determine the critical path and the project duration. В E A 2 F H Start Finisharrow_forward19. Shown below is a mass haul diagram. Determine the free haul volume. a) 1000 m³ c) 2000 m² b) 2500 m² d) 4500 m² 20. Determine a) 1000 m² the volume of waste in item 19. a) 1000 m² b) 2500 m² c) 2000 m² d) 4500 m³arrow_forward
- List the two categories of site cleanup that have to be considered in an estimate, and describe how each category is priced.arrow_forwardA landfill project requires 5000 m3 of compacted soil. The void index specified for the compacted landfill is 0.7. Three borrowing areas are available as indicated in Table 1, which relates the respective soil void rates and the cost per cubic meter of soil transport for the proposed construction site. Carry out the necessary calculations to select the borrowing area from which soil should be brought in to minimize costs. Assume Gs of 2.6 for all areas loan. Table 1 presents the data.arrow_forwardThe ff data represents a single summit mass diagram of a proposed expansion of the Tolosa Expressway. *solve in 3 DECIMAL PLACES* Determine: a) Compute the volume of waste b) compute the volume of borrowarrow_forward
- Q.provide the correct solution for this problem.arrow_forwardA road is being proposed to facilitate a housing development on a scenic Two alternatives have been suggested. One of the roadway alignments is to go around the lake and slightly impact a wetland. The second alternative will also go around the lake and will significantly impact two wetlands. The following table shows the anticipated costs for each alternative. Assuming that the annual interest rate (i) is 7%, determine which alternative is preferred using the Net Present Value method. Alternative First Cost ($) Annual Maintenance ($) Service Life (Years) Salvage Value ($) Annual Wetland Rehabilitation Costs ($) Annual Roadway Lighting Costs ($) I 75,000 3000 15 45,000 7500 1500 II 125,000 2000 15 25,000 2500 2500arrow_forwardThe company wants to locate a new machine tool in a maintenance department. Suppose that there are 5 existing machines that have a material handling relationship with the new machine and are located at the following points (see the second column of the table). The number of trips in a day between the new machine and the existing machines are in the third column of the table. Find the optimum location for the new machine using the Median Method. Suppose it is not possible to place the new machine at the point found in part a. Find and draw the contour lines for (2. 6). Fir a) b) Hospital Coordinates (x, y) Number of trips 1,5 1,4 2,3 4 3.5 4,4 2arrow_forward
- For the network shown below, find the critical path and project duration. Calculate ES, LS, EF, LF, Float for each activity in a tabular form. 2 D A 3 3. В E H 1 3 4 3 7 C 8. 2 G 4 4 2 Critical Path is [.... ] Total Project Duration Units starrow_forward(b) Annual cash fl (c) Rate of return analysis -66 Two hazardous environment facilities are being evaluated, with the projected life of each facility being 10 years. The company uses a MARR of 15%. Using rate of return analysis, which alternative should be selected? Alt. A Alt. B $615,000 $300,000 10,000 158,000 First cost O&M cost 25,000 92,000 Annual benefits Salvage value 65,000 -5,000arrow_forwardTwo underground mines are to be compared to each other in terms of Fatality Injury Frequency Rating (FIFR). In mine A, yearly production is 12 million tonnes of ore and the number of fatality is 3. In mine B, yearly production is 4 million tonnes of ore and the number of fatality is 2. The equation is: FIFR=(Number of Fatalitiesx10)/(Yearly tonnage) What is the interpretation based on FIFR? O a. Both of them are very bad equally. O b. Both of them are very good equally. OC Mine B has a better rating. Od. Mine A has a better rating. O e No comparison can be made by using FIFR because the productions are not equal to each other.arrow_forward
 Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage,
Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage,

