
Concept explainers
The diagrams at right show two identical gliders that move to the right without friction. The hands exert identical, horizontal forces on the gliders. The second glider experiences an additional, smaller force from a massless string held as shown.
Suppose the gliders move through identical displacements.
Is the work done on glider 1 by the hand greater than, less than, or equal to the work done on glider 2 by the hand? Explain.
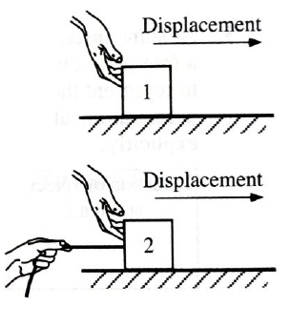
Is the change in kinetic energy of glider 1 greater than, less than, or equal to the change in kinetic energy of glider 2? Base your answer on your knowledge of the net work done on each object.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 3 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
Essential University Physics: Volume 2 (3rd Edition)
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Sears And Zemansky's University Physics With Modern Physics
- Two blocks are connected by a very light string passing over a massless and frictionless pulley (Figure 1). Traveling at constant speed, the 20.0 N block moves 75.0 cm to the right and the 12.0 N block moves 75.0 cm downward. Part E During this process, how much work is done on the 20.0 N block by friction? Express your answer with the appropriate units. HÀ ? W1, 20.0 N = Value J Submit Request Answer Figure Part F 20.0 During this process, how much work is done on the 20.0 N block by the normal force? N Express your answer with the appropriate units. HẢ ? 12.0 N W. 1, 20.0 N = Value Jarrow_forwardTwo blocks are connected by a very light string passing over a massless and frictionless pulley (Figure 1). Traveling at constant speed, the 20.0 N block moves 80.0 cm to the right and the 12.0 N block moves 80.0 cm downward. Part E During this process, how much work is done on the 20.0 N block by friction? Express your answer with the appropriate units. HẢ ? Wf, 20.0 N = Value Units Figure 1 of 1 Submit Request Answer Part F 20.0 During this process, how much work is done on the 20.0 N block by the normal force? N Express your answer with the appropriate units. ? 12.0 N Wn, 20.0 N = Value Unitsarrow_forwardAnswer the following questions based in Energy Skate Park Experiment: Calculate the ratio of the mechanical energy at B and mechanical energy at A (EB/EA) and (EC/EB).What do these ratios tell you about the conservation of energy? Is the mechanical energy conserved between A and B? Explain Is the mechanical energy conserved between B and C? Explainarrow_forward
- Please answer all 3 subparts. 1. A robot begins pushing a 10kg box that was already moving at 0.5m/s [Right] along a surface with a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.15. The robot pushes with only 30N [Right] of force. a) What is the acceleration of the box? b) Using the Work-Energy theorem, calculate how much work the robot does on the box accelerating it from 0.5m/s [Right] to 2m/s [Right]. c) What distance did the robot push the box? Use kinematics to check your work.arrow_forwardA force of 8 N will stretch a rubber band 4 cm (0.04 m). Assuming that Hooke's law applies, how far will a 12-N force stretch the rubber band? How much work does it take to stretch the rubber band this far? How far will a 12-N force stretch the rubber band? m (Simplify your answer.) How much work does it take to stretch the rubber band this far? J (Simplify your answer.)arrow_forwardPROBLEM SET # 10: WORK DONE BY A VARYING FORCE On the space provided, present correct and organized solutions to the following answered problems. Box the final answers. Detach each page neatly and submit to your instructor. 1. A particle was subjected to a force F, that varies with position as described by the F vs. x graph below. How much work was done by the force on the body as it moves from x = 0 to x = 10.0 m? (Ans: 22.5 J) 4.00 3.00 F N 2.00 1.00 0.00 0.0 5.0 10.0 15.0 X, marrow_forward
- PROBLEM SET # 9: WORK DONE BY A CONSTANT FORCE On the space provided, present correct and organized solutions to the following answered problems. Box the final answers. Detach each page neatly and submit to your instructor. 2. An 8.5-kg block is pushed along a horizontal rough surface by a 40-N force inclined at 20° with the horizontal. The coefficient of friction between the surface and block is 0.35. If the block has an initial velocity of 3.6 m/s and the force does 200 J of work on the block, find: (a) The total distance moved by the block. (Ans: 5.32 m) (b) The final velocity of the block. (Ans: 4.85 m/s)arrow_forwardA force F is applied to a 2.0 kg, radio-controlled model car parallel to the x-axis as it moves along a straight track. The x-component of the force varies with the x-coordinate of the car as shown in the figure (Figure 1). Part A Calculate the work done by the force F when the car moves from x = 0 to x = 3.0 m. Express your answer with the appropriate units. Wo-3.0 = Value Units Figure 1 of 1 Part B F, (N) Calculate the work done by the force F when the car moves from x = 3.0 m to x = 4.0 m. 2 Express your answer with the appropriate units. 1 x (m) ? 1 2 3 4 5 -1 W3.0–4.0 = Value Units -2arrow_forwardWrite an expression for the net external work done on the block as it moves from the bottom of the block) and H (the height of the ramp). Show your work. to the top of the ramp in terms of the following quantities: mg (the magnitude of the weight| Name Work and changes in kinetic energy Me HL Free-body diagram for block H . In the space provided, draw and label a free-body diagram for the block as it moves un the ramp. h. For each force on the block, determine the angle between the displacement of the block and the force as the block moves up the ramp. Write an expression for the work done on the block by each force as the block moves up the I6 Express your answer in terms of any or all of the following: sin 0, cos 0, m, g, and d. the k done by any force is zero, state so explicitly. Show your work. You may need to use the angle addition formula cos (a + B) = cos a cos B- sin a sin p.arrow_forward
- Whenever the answer to the "is it above or below the zero reference for height?" question is Yes, then it has gravitational potential energy at that point. If the answer is No, then its gravitational potential energy at that point is zero. In the space below, draw the LOL diagram for the cart + block motion. The first Lis for energies at the initial point of the motion. The O is for transfers of energy (by macroscopic forces doing work or microscopic interactions transferring energy through heat). The second Lis for energies at the final point of the motion. EKi Egi Esi Egf Eg A Epharrow_forwardC. Suppose the resultant force acted on an object that was at the origin and resulted in the displacement vector d =. How much work was done by the resultant force on the object? Use your answer from part b as appropriate. d. Using your results from parts b and c, what is the measure of the angle between the resultant force and displacement vector?arrow_forwardThe total mass of a rollercoaster is 650 kg. Use the measurments in the image and your knowledge of conservation of energy to answer the following questions: 1) Use the law of conservation to find the speed of the rollercoaster at point B 2) If it takes the motor 20.0 s to pull the rollercoaster to point A, fing the power of the motor. 3) In real life, some of the energy the roller coaster has at point A will be lost as thermal energy due to friction as it travels through the track. If the speed of the roller coaster at point C is only 19 m/s, calculate the amount of energy that was lost due to friction.arrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
