
Concept explainers
(a)
The linear atomic density of atom.
(a)
Answer to Problem 60AAP
The linear atomic density of atom is
Explanation of Solution
Draw the figure for the plane of
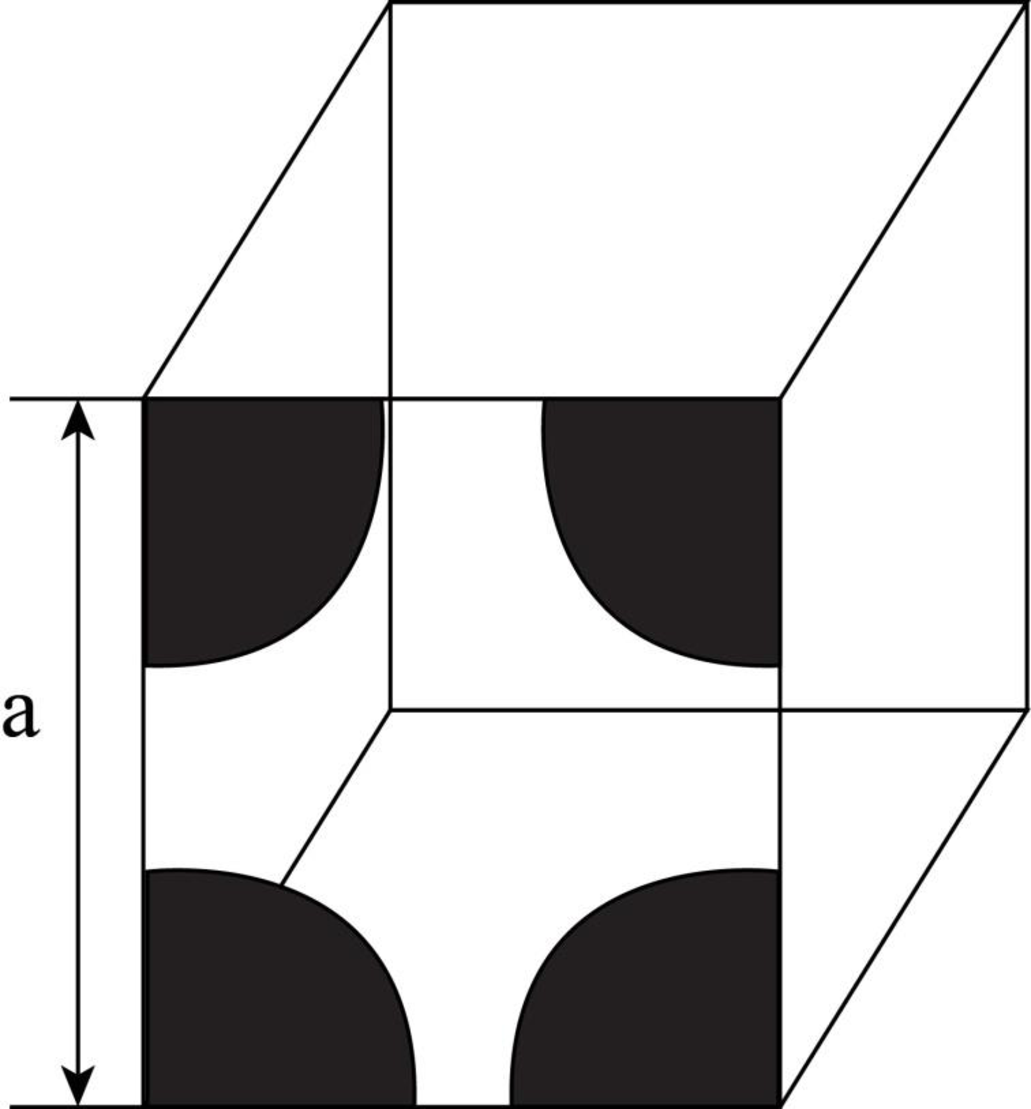
Figure-(1)
Write the expression for the planer density of the atom.
Here, the number of the atoms is
Conclusion:
Here, the number of atoms for
Substitute
Thus, the linear atomic density of atom is
(b)
The linear atomic density of atom.
(b)
Answer to Problem 60AAP
The linear atomic density of atom is
Explanation of Solution
Draw the figure for the plane of
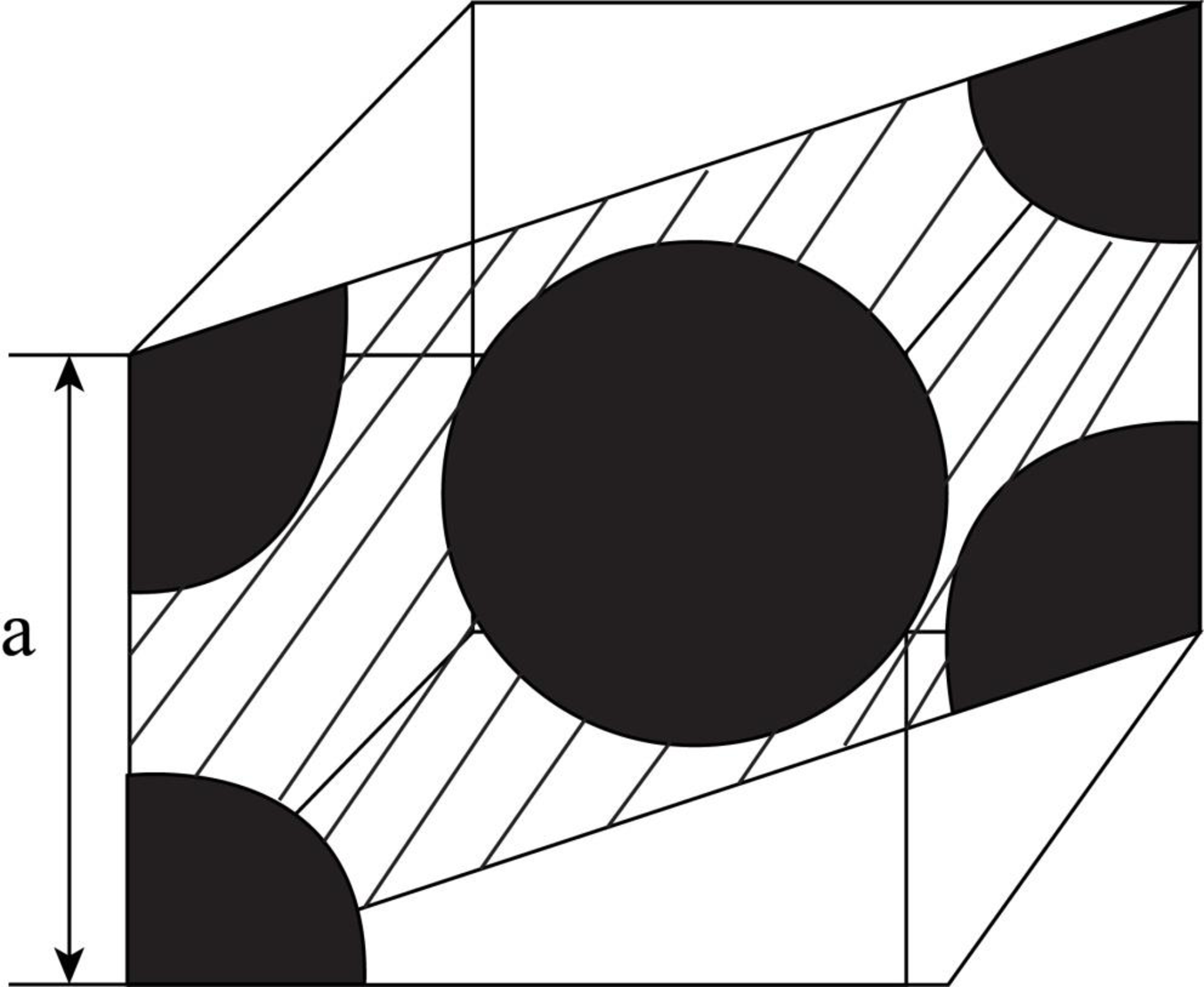
Figure (2)
Write the expression for the planer density of the atom.
Here, the number of the atoms is
Conclusion:
Here, the number of atoms for
Substitute
Thus, the linear atomic density of atom is
(c)
The linear atomic density of atom.
(c)
Answer to Problem 60AAP
The linear atomic density of atom is
Explanation of Solution
Draw the figure for the plane of
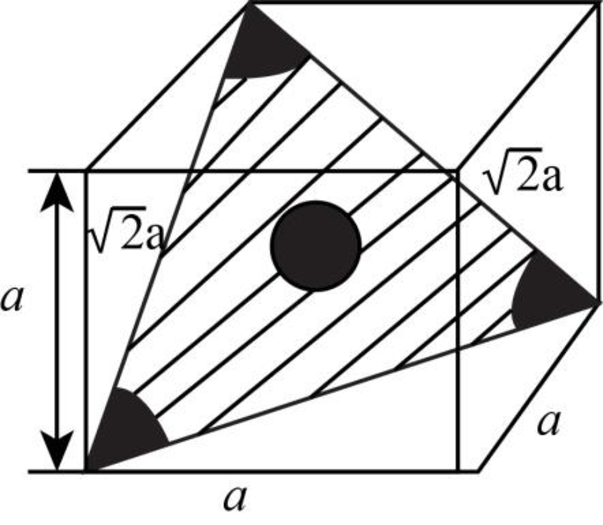
Figure-(3)
Write the expression for the planer density of the atom.
Here, the number of the atoms is
Conclusion:
Here, the number of atoms for
Substitute
Thus, the linear atomic density of atom is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Foundations of Materials Science and Engineering
- 4. Figure out the indexes of the following lattice planes. (The arrows are the basic vectors of the lattice.) (a) (b) (c)arrow_forwardPlatinum is a metal having a FCC crystal structure with a density p= 21.45 kg/m3. Calculate the lattice constant for this crystal as well as the atomic radius of platinumarrow_forwardSolve the following Problem * Iodine has an orthorhombic unit cell for which the a, b, and c lattice parameters are 0.479, 0.725, and 0.978 nm, respectively. (a) If the atomic packing factor and atomic radius are 0.547 and 0.177 nm, respectively, de- termine the number of atoms in each unit cell. (b) The atomic weight of iodine is 126.91 g/mol; compute its theoretical density.arrow_forward
- Silver Ag has the fcc crystal structure as shown in the figure below. Determine its atomic packing factor APF? Given: The radius of Germanium: r(Ag)= 0.144 nm.  Select one: a. 0.14 b. 0.34 c. 0.68 d. 0.12 e. 0.4 f. 0.51 g. 0.74 h. 0.21arrow_forwardThe spacing of adjacent atoms in a NaCl crystal is 0.282 nm, and the masses of the atoms are 3.82*10-26 kg (Na) and 5.89*10-26 kg (CI). Use this information to calculate the density of NaCl. p= kg/m³arrow_forwardA Lanthanum (atomic mass 138.91 g/mol) sample has a lattice parameter 3.77Å. Assume it contains 514 vacancies per 200 unit cells. Calculate (a) the number of vacancies per cm³, (b) density of the sample and (c) compare the number of vacancies per unit cell between the sample given and a perfect Lanthanum sample. Assume T=400C.*arrow_forward
- Silver Ag has the fcc crystal structure as shown in the figure below. Determine its atomic packing factor APF? Given: The radius of Germanium: rAg= 0.144 nm. Select one: Oa. 0.68 Ob.0.34 Od.o.14 te.0.74 1012 g.0.21 h.0.51arrow_forwardVanadium (V) has a BCC crystal structure. The atomic radius is R = 0.132 nm and the atomic mass is M = 50.94 g/mole. What is the density of Vanadium in g/mm ? Given: Avogadro's Number NA = 0.6023 x 1024 (atoms/mole) Select one: O a, 0.021 O b. 0.011 Oc.1.5 d. 0.0087 e. 0.00597 Potassium (K) has the Body-Centered Cubic (BC) crystal structune. The edge length is a = 0.533 nm. What is the linear density in atoms/nm along direction (01112 Select one: O ENG O O 0 00arrow_forwardWith the information on its molar volume and lattice parameter, a, determine the crystal structure of Puterium. Sketch the crystal structure indicating the atoms arrangement. DATA: molar volume, Vmol = 5.90 cm/mol; lattice parameter, a = 2.15 Å = 2.15 x 10-8 cmarrow_forward
- Niobium has a BCC crystal structure, an atomic radius of 0.143 nm and an atomic weight of 92.91 g/mol. Calculate the theoretical density for Nb. i g/cm³arrow_forwardIron exhibits an allotropic behavior change of solid state structure in such a way that when it is heated to 910 C it undergoes a structure change from body-centered cubic BCC to face-centered cubic FCC considering that the atomic radius of iron increases to 0.1241 nm or 0.126 nm more when said temperature is reached obtainThe volume change experienced by the structure when the temperature of 910 C is reachedarrow_forwardCalculate the surface density of the lattice atoms that lie on the (100) plane of an FCC crystal??? Please solve it quickly by handwrittenarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





