
Concept explainers
The stopping distance of the car measured along the incline.
Answer to Problem 45P
The stopping distance of the car measured along the incline is
Explanation of Solution
Figure 1 represents the free body diagram of car on level ground.
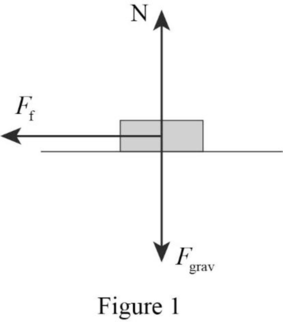
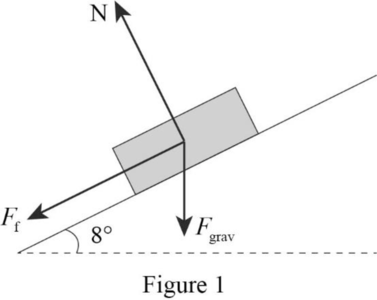
Figure 1 represents the free body diagram of car on the incline .
Write the
Here,
Write the expression for net force acting on the car.
Here,
Write the expression for kinetic friction force.
Here,
The above equation can be written as
The net force acting on the level car is opposite to the friction force.
Rearrange the above equation.
Since the car on the level ground is at rest, equation (I) is written as
Use the above equation in equation (IV).
Write the acceleration of the object down an incline from equation.
Here,
Use the above equation in equation (V).
Write the kinematic equation of the car in inclined motion.
Here,
Since the final velocity of the car in inclined motion is zero, the above equation is written as
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the stopping distance of the car measured along the incline is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
College Physics, Volume 1
- An arrow is shot from 5 ft above the top of a hill with a vertical upward velocity of 104 ft/s. If it strikes the plain below after 9.5 s, how high is the hill? If the arrow is launched at t 0, then write an equation describing velocity as a function of time. v(t) = 104 - 32t The hill is ft tall.arrow_forwardAn object is launched at a velocity of 25 m/s in a direction making an angle of 48 degrees upward with the horizontal. How high was the object before it achieved free fall?arrow_forwardSuppose a chinook salmon needs to jump a waterfall that is 1.44 m high. (a) If the fish starts from a distance 1.07 m from the base of the ledge over which the waterfall flows, find the x- and y-components of the initial velocity the salmon would need to just reach the ledge at the top of its trajectory. v0x = ? m/s v0y = ? m/sarrow_forward
- An object is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of +5 m/s and then comes back down. What is the final velocity when it returns to its initial height? Ignore air resistance.arrow_forwardA car drives horizontally off of a 6.60 m tall cliff. The car lands 7.39 m from the base of the cliff. Assuming air resistance can be ignored, at what speed did the car leave the top of the cliff and at what speed is the car traveling just before striking the ground?arrow_forwardAs the first human astronaut to land on a distant planet, you are standing on the edge of a small cliff. You toss a small experiment apparatus straight up in the air and it reaches a maximum height of 3.0 m above the cliff. The apparatus then falls to the bottom of the cliff, landing a distance 10 m below its initial position. Given that the acceleration due to gravity on the exoplanet is a = -5.6j m/s?, how long did it take for the apparatus to get from the top of its trajectory to the bottom of the cliff? The coordinate system is set up such that "up" is in the +j direction. Pick the correct answer 1.9 s O 1.5 s 1.3 s O 2.2 s O 1.0 sarrow_forward
- A golf ball rolls off with an angle of - 15° from a cliff with an initial speed of Vj =13.5 m/s. The ball falls a vertical distance of h = 25.9 m into a lake below. How much time does the ball spend in the air?arrow_forwardA bus driver heads south with a steady speed of v, = 20.0 m/s for t, = 3.00 min, then makes a right turn and travels at v, = 25.0 m/s for t, = 2.40 min, and then drives northwest at v3 = 30.0 m/s for t3 = 1.00 min. For this 6.40-min trip, calculate the following. Assume +x is in the eastward direction. (a) total vector displacement (Enter the magnitude in m and the direction in degrees south of west.) magnitude m direction o south of west (b) average speed (in m/s) m/s (c) average velocity (Enter the magnitude in m/s and the direction in degrees south of west.) magnitude m/s direction O south of westarrow_forwardA bus driver heads south with a steady speed of v, = 20.0 m/s for t, = 3.00 min, then makes a right turn and travels at v, = 25.0 m/s for t, = 2.40 min, and then drives northwest at v3 = 30.0 m/s for t3 = 1.00 min. For this 6.40-min trip, calculate the following. Assume +x is in the eastward direction. (a) total vector displacement (Enter the magnitude in m and the direction in degrees south of west.) magnitude direction (b) average speed (in m/s) (c) average velocity (Enter the magnitude in m/s and the direction in degrees south of west.) magnitude directionarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
