
a.
To calculate: The EPS of Lopez-Portillo Company before the expansion, if EBIT is 9% on total assets.
Introduction:
Earning per share (EPS):
It is the profit per outstanding share of a public company. A higher EPS indicates higher value of the company because investors are ready to pay higher price for one share of the company.
a.
Answer to Problem 25P
The calculation of EPS of current plan, plan D, and plan E of Lopez-Portillo Company is shown below.
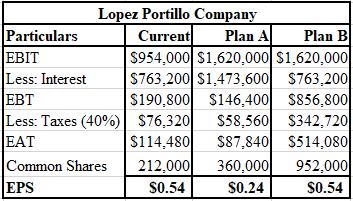
Explanation of Solution
The formulae used for the computation of EPS of current plan, plan D, and plan E are shown below.
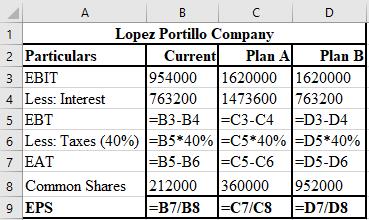
Working notes:
Calculation of interest on current plan:
Calculation of common shares of current plan:
Calculation of interest of plan A:
Calculation of common shares of plan A:
Calculation of common shares of plan B:
Note : The interest of plan B is unchanged.
b.
To calculate: The DFL of Lopez-Portillo company of each plan.
Introduction:
Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL):
It refers to the leverage ratio that evaluates the company’s EPS to the variations in its operating income. This ratio indicates that higher DFL leads to the higher earnings of the firm.
b.
Answer to Problem 25P
The DFL of current plan is 5 times , plan A is 11.07 times, and plan B is 1.89 times.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of DFL of current plan:
Computation of DFL of plan A:
Computation of DFL of plan B:
c.
To calculate: The EPS of each Plan and also determine the impact of each plan of Lopez-Portillo company.
Introduction:
Earning per share(EPS):
It is the profit per outstanding share of a public company. A higher EPS indicates higher value of the company because investors are ready to pay higher price for one share of the company.
c.
Answer to Problem 25P
The calculation of EPS of plan A and plan B of Lopez-Portillo Company is shown below.
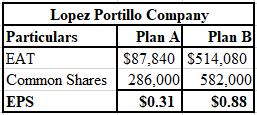
Explanation of Solution
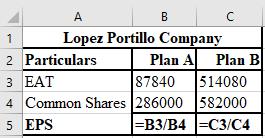
The formula used for the computation of EPS of Plan A and Plan B are shown below.
Plan B will provide a higher EPS on a constant basis.
Working notes:
Calculation of common shares of plan A:
Calculation of common shares of plan B:
d.
To explain: The reason behind the concern of CFO about the stock values of Lopez-Portillo Company.
Introduction:
Share price:
The highest price of one share of a company that an investor is willing to pay is termed as the share’s price. It is the current price used for the trading of such shares.
d.
Answer to Problem 25P
The CFO of the company is concerned about the value of the stock because it impacts capital budgeting decisions and it also influences the ability to finance projects.
Explanation of Solution
The reason behind CFO’s concern about the common stock values are as follows:
(a) Common stock creates shareholder’s wealth.
(b) It impacts the capital budgeting decisions.
(c) It also influences the potential of financing any undertaken projects either at a high or low cost of capital.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Foundations of Financial Management Format: Loose-leaf
- Ohio Quarry Inc. has $10 million in assets. Its expected operating income (EBIT) is $4 million and its income tax rate is 40 percent. If Ohio Quarry finances 20 percent of its total assets with debt capital, the pretax cost of funds is 13 percent. If the company finances 40 percent of its total assets with debt capital, the pretax cost of funds is 18 percent. Round your answers to the questions below to two decimal places. Determine the rate of return on equity (ROE) under the three different capital structures (0, 20, and 40% debt ratios).0% debt ratio: % 20% debt ratio: % 40% debt ratio: % Which capital structure yields the highest expected ROE?-Select-0 percent debt and 100 percent equity20 percent debt and 80 percent equity40 percent debt and 60 percent equityItem 4 yields the highest expected ROE. Determine the ROE under each of the three capital structures (0, 20, and 40% debt ratios) if expected EBIT decreases by 30 percent.0% debt ratio: % 20% debt ratio: %…arrow_forwardOhio Quarry Inc. has $10 million in assets. Its expected operating income (EBIT) is $4 million and its income tax rate is 40 percent. If Ohio Quarry finances 20 percent of its total assets with debt capital, the pretax cost of funds is 13 percent. If the company finances 40 percent of its total assets with debt capital, the pretax cost of funds is 18 percent. Round your answers to the questions below to two decimal places. Determine the percentage change in ROE under each of the three capital structures (that is, debt ratios) as the result of a 30 percent decline in EBIT. Use the minus sign to enter a negative percentage change in ROE if necessary.0% debt ratio: % 20% debt ratio: % 40% debt ratio: %arrow_forwardDickinson Company has $12,020,000 million in assets. Currently half of these assets are financed with long-term debt at 10.1 percent and half with common stock having a par value of $8. Ms. Smith, Vice President of Finance, wishes to analyze two refinancing plans, one with more debt (D) and one with more equity (E). The company earns a return on assets before interest and taxes of 10.1 percent. The tax rate is 40 percent. Tax loss carryover provisions apply, so negative tax amounts are permissable. Under Plan D, a $3,005,000 million long-term bond would be sold at an interest rate of 12.1 percent and 375,625 shares of stock would be purchased in the market at $8 per share and retired. Under Plan E, 375,625 shares of stock would be sold at $8 per share and the $3,005,000 in proceeds would be used to reduce long-term debt. a. How would each of these plans affect earnings per share? Consider the current plan and the two new plans. b-1. Compute the earnings per share if return on…arrow_forward
- Edsel Research Labs has $28.20 million in assets. Currently half of these assets are financed with long-term debt at 5 percent and half with common stock having a par value of $10. Ms. Edsel, the Vice President of Finance, wishes to analyze two refinancing plans, one with more debt (D) and one with more equity (E). The company earns a return on assets before interest and taxes of 5 percent. The tax rate is 30 percent. Under Plan D, a $7.05 million long-term bond would be sold at an interest rate of 7 percent and 705,000 shares of stock would be purchased in the market at $10 per share and retired. Under Plan E, 705,000 shares of stock would be sold at $10 per share and the $7,050,000 in proceeds would be used to reduce long-term debt. a-1. How would each of these plans affect earnings per share? Consider the current plan and the two new plans. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Earnings per Share Current Plan D Plan E a-2. Which…arrow_forwardes Edsel Research Labs has $26.40 million in assets. Currently half of these assets are financed with long-term debt at 6 percent and ha with common stock having a par value of $10. Ms. Edsel, the Vice President of Finance, wishes to analyze two refinancing plans, one with more debt (D) and one with more equity (E). The company earns a return on assets before interest and taxes of 8 percent. The tax rate is 30 percent. Under Plan D, a $6.60 million long-term bond would be sold at an interest rate of 8 percent and 660,000 shares of stock would be purchased in the market at $10 per share and retired. Under Plan E, 660,000 shares of stock would be sold at $10 per share and the $6,600,000 in proceeds would be used to reduce long-term debt. a-1. Compute earnings per share considering the current plan and the two new plans. Note: Round your answers to 2 decimal places. Current Plan D Plan E Earnings per Share $ $ $ 0.42 0.20 1.26 a-2. Which plan(s) would produce the highest EPS? Note that…arrow_forwardQuigley Inc. is considering two financial plans for the coming year. Management expects sales to be $335,000, operating costs to be $290,000, assets (which is equal to its total invested capital) to be $210,000, and its tax rate to be 25%. Under Plan A it would finance the firm using 25% debt and 75% common equity. The interest rate on the debt would be 8.8%, but under a contract with existing bondholders the TIE ratio would have to be maintained at or above 4.2. Under Plan B, the maximum debt that met the TIE constraint would be employed. Assuming that sales, operating costs, assets, total invested capital, the interest rate, and the tax rate would all remain constant, by how much would the ROE change in response to the change in the capital structure? Do not round your intermediate calculations.arrow_forward
- The Haris - Arshi Company is attempting to establish a current assets polıcy. Company has allocated $900,000 to fixed assets and the firm plans to maintain a 50 percent debt to assets a ratio. The interest rate is 10% on all debts. Company is considering three alternative current asset policies: this can be 40, 50 or 60 percent of projected sales. The company expects to earn 20 percent profit before interest and taxes on sales of $3 million. Company's effective federal-plus-state-tax rate is 15 percent. What is the expected return on equity under each alternative? Drawa descriptive conclusion for each Current ASset Investment Policy.arrow_forwardKelly Corporation is considering the issuance of either debt or preferred stock to finance the purchase of a facility costing P1.5 million. The interest rate on the debt is 16 percent. Preferred stock has a dividend rate of 12 percent. The tax rate is 46 percent. REQUIREMENTS: 1. What is the annual interest payment? 2. What is the annual dividend payment? 3. What is the required income before interest and taxes to satisfy the dividend requirement??arrow_forwardRefi Corporation is planning to repurchase part of its common stock by issuing corporate debt. As a result, the firm's debt-equity is expected to rise from 35 percent to 50 percent. The firm currently has $2.7 million worth of debt outstanding. The pretax cost of debt is 6.4 percent. The firm expects to have an aftertax earnings of $940,000 per year in perpetuity. The corporate tax rate is 21 percent. a. What is the expected return on the equity before the repurchase agreement? b. What is the return on assets for the firm? (Hint: use the MM Proposition ll with Tax.) c. What is the expected return on the firm's equity after the repurchase announcement? d. What is the weighted-average cost of capital for the company after the repurchase announcement?.arrow_forward
- Blue Co. uses Additional Funds Needed as a plug item. It has a new capital budget of P1,450,000, a profit of P705,000 and a dividend payout of 25%. Assuming that any additional financing need will be funded by issuance of long-term bonds, how much bonds must be raised?arrow_forwardShip Shape Marine (SSM) needs $92 million to support future growth. If SSM issues bonds to raise funds, flotation (issuance) costs will be 8 percent. Each bond will be sold for $1,000; fractions of bonds cannot be issued. How many bonds must be issued so that SSM has $92 million after flotation costs to use for its planned growth?108,00092,00084,64099,360100,000arrow_forwardThe Calgary Company is attempting to establish a current assets policy. Fixed assets are $600,000, and the firm plans to maintain a 40 percent debt-to-assets ratio. Calgary has no operating current liabilities. The interest rate is 12 percent on all debt. Three alternative current asset policies are under consideration: 40, 50, and 60 percent of projected sales. The company expects to earn 18 percent before interest and taxes on sales of $6 million. Calgary’s effective tax rate is 40 percent. Questions What is the expected return on equity under each alternative and why current assets policy is important in this particular situation? Evaluate ROE from owner point of view and suggest which option is best for him? Suggest which option would you like if you are managers of the company and do not have much concern about business?arrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
