
Concept explainers
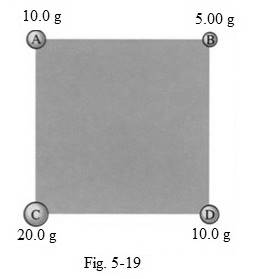
The center of mass of the particles which are positioned at the corners of a square with length of sides measuring
Answer to Problem 30P
Position of center of mass
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Mass of particle A
Mass of particle B
Mass of particle C
Mass of particle D
Length of side of square
Formula used:
The x and y coordinates, of the center of mass of particles of a system in a two dimensional plane is calculated by the following formula:
Wherein
Similarly the y coordinates are given by the following formula:
Wherein
The position of center of mass of a particle having x and y coordinate is given by the formula:
Wherein r is the position of center of mass of the particle, while
Calculation:
As per figure 5-19, the x and y coordinates of position of mass at A is
Similarly the x and y coordinates for the position of mass at B, C and D respectively are
Substituting the various values of masses of particles at points A, B, C and D and also its horizontal distances from origin in the equation:
Similarly substituting the various values of masses of particles at points A, B, C and D and also its vertical distances from origin in the equation:
The position of center of mass is given by the formula:
Substituting
Conclusion:
The x and y coordinates of the particles are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Physics Fundamentals
- Find the center of mass of a cone of uniform density that has a radius R at the base, height h, and mass M. Let the origin be at the center of the base of the cone and have +z going through the cone vertex.arrow_forwardWhere is the center of mass of a slice of pizza that was cut into eight equal slices? Assume the origin is at the apex of the slice and measure angles with respect to an edge of the slice. The radius of the pizza is R.arrow_forwardWhere is the center of mass of a semicircular wire of radius R that is centered on the origin, begins and ends on the x axis, and lies in the x, y plane?arrow_forward
- Find the center of mass of a rectangular material of length a and width b made up of a material of nonuniform density. The density is such that when the rectangle is placed in the xy-plane, the density is given by (x,y)=0xy .arrow_forwardFind the center of mass of a rectangular block of length a and width b that has a nonuniform density such that when the rectangle is placed in the x, y-plane with one corner at the origin and the block placed in the first quadrant with the two edges along the x- and y-axes, the density is given by (x,y)=0x , where 0 is a constant.arrow_forwardFind the center of mass of a rod of length L whose mass density changes from one end to the other quadratically. That is, if the rod is laid out along the x-axis with one end at the origin and the other end at x=L , the density is given by (x)=0+(10)(xL)2 , where 0 and 1 are constant values.arrow_forward
- Two particles of masses m1 and m2 , move uniformly in different circles of radii R1 and R2 R2 about origin in the x, y-plane. The x- and y-coordinates of the center of mass and that of particle 1 are given as follows (where length is in meters and tin seconds): x1(t)=4cos(2t) , y1(t)=4sin(2t) and: xCM(t)=4cos(2t) , yCM(t)=3sin(2t) . a. Find the radius of the circle in which particle 1 moves. b. Find the x- and y-coordinates of particle 2 and the radius of the circle this particle moves.arrow_forwardA thin wire is bent into the shape of a semicircle x² + y² = 4, x ≥ 0. If the linear density is a constant k, find the mass and center of mass of the wire.arrow_forwardA lamina occupies the part of the disk x2 + y2 ≤ 1 in the first quadrant. Find the center of mass of the lamina if the density at any point is proportional to the square of its distance from the origin. (x, y) = (__,__)arrow_forward
- A cubical box, open at the top, with edge length 36 cm, is constructed from metal plate of uniform density and negligible thickness (see the figure). Find the z-coordinate of the center of mass of the box ( cm).arrow_forwardFind the mass and the indicated coordinates of the center of mass of the solid region Q of density p bounded by the graphs of the equations. Find y using p(x, y, z) = ky. Q: 3x + 3y + 6z = 18, x = 0, y = 0, z = 0arrow_forwardIf the center of mass of three objects in the xy-plane is given by the location (3 cm, 4 cm) and two of theobjects have the following mass and locations: 5 kg at (3,2), 2 kg at (1, 3) and the third object has mass 8 kg,find the location of the third object.arrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
