
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Two most stable Lewis structures for thiocyanate ion are to be written and the atom in each of them that bears a formal charge
Concept introduction:
The formal charge of an atom is calculated by the following formula:
Thiocyanate ion is a good nucleophile and reacts with a primary
Constitutional isomers have the same molecular formula but differ in the connectivity of atoms in their structure.
Answer to Problem 23P
Solution:
a) The stable Lewis structures for thiocyanate ion are:
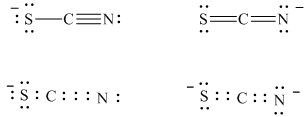
In structure I, the sulfur atom has a formal charge of
b) The structures of the two constitutional isomers of

Explanation of Solution
a) Thiocyanate ion,
The total number of valence electrons in
The two stable Lewis structures of the thiocyanate ion are shown below:
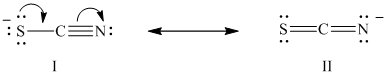
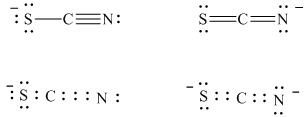
Carbon belongs to Group
In structure I, the electron counts and formal charge for each atom are as follows:
Hence, in structure I, the sulfur atom has a formal charge of
In structure
Hence, in structure
b)
In the reaction given, the alkyl halide is a primary alkyl bromide. The nucleophile is thiocyanate ion, formed by the dissociation of
Thiocyanate ion has two nucleophilic centers, which means it can attack through either sulfur or nitrogen atom. Because of this, when thiocyanate is used as a nucleophile, two possible products are obtained. In one product, the nucleophile attacks through the sulfur atom and gets attached to the carbon atom in the alkyl halide. In the other product, the nucleophile attacks through the nitrogen atom and gets attached to the carbon atom in the alkyl halide. The molecular formula of both the products remains the same; only the connectivity of atoms is different. Hence, they form constitutional isomers as follows:
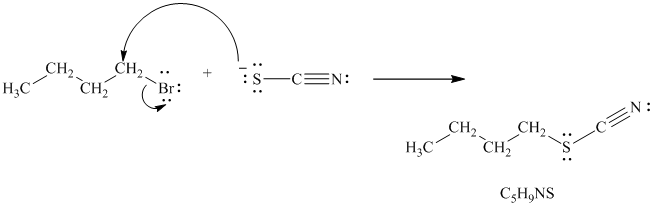
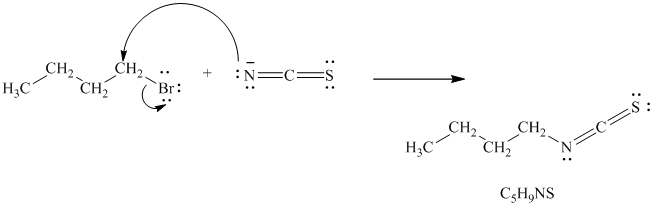
Thus, the structures of the two constitutionally isomeric products of the molecular formula

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- Name the following compounds A and B. How could you distinguish these two molecules by using 1H NMR and IR techniques? Propose an analytical technique to determine the iron content of these compounds. Calculate the mass percentages of C and H of compound B (C: 12.01 g/mol; H: 1.008 g/mol; Fe: 55.845 g/mol).arrow_forward10. M and N are amines with the molecular formula C3H»N. Reaction of M with sodium nitrite and HCI releases nitrogen gas and produces a mixture of X and Y and Propanol while N produces a yellowish oily compound, S when reacted with the same reagents. Give the structures of M, N, X, Y, and S. Outline the synthesis of M from a suitable alkene.arrow_forwardA task is assigned to an undergraduate student to test two samples (known as compounds K and L) in the laboratory. She placed these two compounds through various scientific tests. She discovered that these compounds have the same molecular formula, CSHSO. When treated with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine, all of these compounds produce brightly coloured precipitate, and both are reduced to an organic compound with the molecular formula C§H100. However, compound K can be easily oxidized by chromic acid to formed compound N and vice versa for compound L. Furthermore, when both compounds react with Fehling's solutions, they produce negative results. However, only compound K forms a silver mirror when it reacts with Tollen's reagent, and compound L does not. Identify the possible structural formulae for compounds K, L, and N by ignoring their position isomerism. Indicate the formation of compound N from compound K. Predict the chemical reaction that occurs when compound L reacts with 2,4-…arrow_forward
- Compounds B and C are isomers with molecular formula C5H9BrO2. The 1H NMR spectrum of compounds B and C are shown below. The IR spectrum corresponding to compound B showed strong absorption bands at 1739, 1225, and 1158 cm-1, while the spectrum corresponding to compound C have strong bands at 1735, 1237, and 1182 cm-1. 1.Based on the information provided, determine the structure of compounds B and C. 2.Assign all peaks in 1H NMR spectrum of compounds B and C.arrow_forwardGive reasons for the following:(i) Aniline does not undergo Friedal-Crafts reaction.(ii) (CH3)2 NH is more basic than (CH3)3 N in an aqueous solution.(iii) Primary amines have higher boiling point than tertiary amines.arrow_forwardThe reaction of Compound B with O3, followed by Me2S gave two products, C and D (Scheme 1). The mass spectrums of products C and D are shown below. Identify the structures of products C and D. Provide explanation for your answer (based on mass spectrometry interpretation).arrow_forward
- Compound p,c6h14O does not react w/sodium metal,doesn't discharge the color of Br2 in ccl4, the H-NMR spectrum shows 2 signal,a 12H doublet at 1.1, and a 2h sextet at 3.6. Propose a structure for this compound,p.arrow_forwardCompound Y (molecular formula C6H10) gives four lines in its 13C NMRspectrum (27, 30, 67, and 93 ppm) and the IR spectrum given here.Propose a structure for Y. Additional spectroscopy problems on alkynes are given in Chapters B and C:Infrared spectroscopy: B.4a; B.5; B.16a; B.19a; B.21a, d; B.29Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: C.12aarrow_forwardSpirocyclic compounds, such as compound 3, are made and used by insects for the purposes of communication. The first step of a synthesis of compound 3 involves treatment of (S)-1,2-epoxypropane (compound 1) with lithium acetylide, followed by acid workup, to give compound 2, as shown below (J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 3054-3065). Identify the structure of compound 2 and provide a mechanism for its formation. (Hint: The carbon-lithium bond reacts in a way that is similar to the carbon-magnesium bond of a Grignard reagent.) 1 13.17 a 1) Li—= 2) H₂O+ нас!!!!!! C5H8O Edit Drawing 2 Ž Modify the given structure of the starting material to draw the major product. an 3arrow_forward
- (a) Tsomane and Nyiko were given a task of synthesising methylenecyclohexane 2. After a brief discussion with each other, Tsomane proposed Method A to synthesise 2 from cyclohexanone 1 while Nyiko proposed Method B that started from hydroxymethylcyclohexane 3. Each student believed that their proposed method is better than the other. (Scheme below) (1) 1 Ph THF A Ph Ph B H₂SO4 100 °C 3 OH What is the name of the reaction that is followed by reaction Method A?arrow_forwardQ1/Do as required: 1-The role of H2SO4 in Preparation of Nitrobenzene. Explain 2- Preparation of Nitrobenzene in cool phase. 3-In an experiment Hydrolysis of Acetanilide What color does the litmus paper change to and why? 4-When acetanilide reacts with bromine (x), acctanilide gives p-bromo acetanil 5- why used strongly alkaline (NaOH)in Preparation of Aniline?arrow_forward(a) Tsomane and Nyiko were given a task of synthesising methylenecyclohexane 2. After a brief discussion with each other, Tsomane proposed Method A to synthesise 2 from cyclohexanone 1 while Nyiko proposed Method B that started from hydroxymethylcyclohexane 3. Each student believed that their proposed method is better than the other. (Scheme below) (1) Ph Ph 8*8 Ph THF A 1 Santande B H₂SO4 100 °C 3 OH Using curly arrows, provide full mechanistic details accounting how methylenecyclohexane 2 was synthesised according to both Methods A and B.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





