
Concept explainers
Owl-Eye Radiologists (OR) does various types of diagnostic imaging. Radiologists perform tests using sophisticated equipment. OR’s management wants to compute the costs of performing tests for two different types of patients: those who are hospitalized (including those in emergency rooms) and those who are not hospitalized but are referred by physicians. The data for June for the two categories of patients follow:

The accountant first assigns
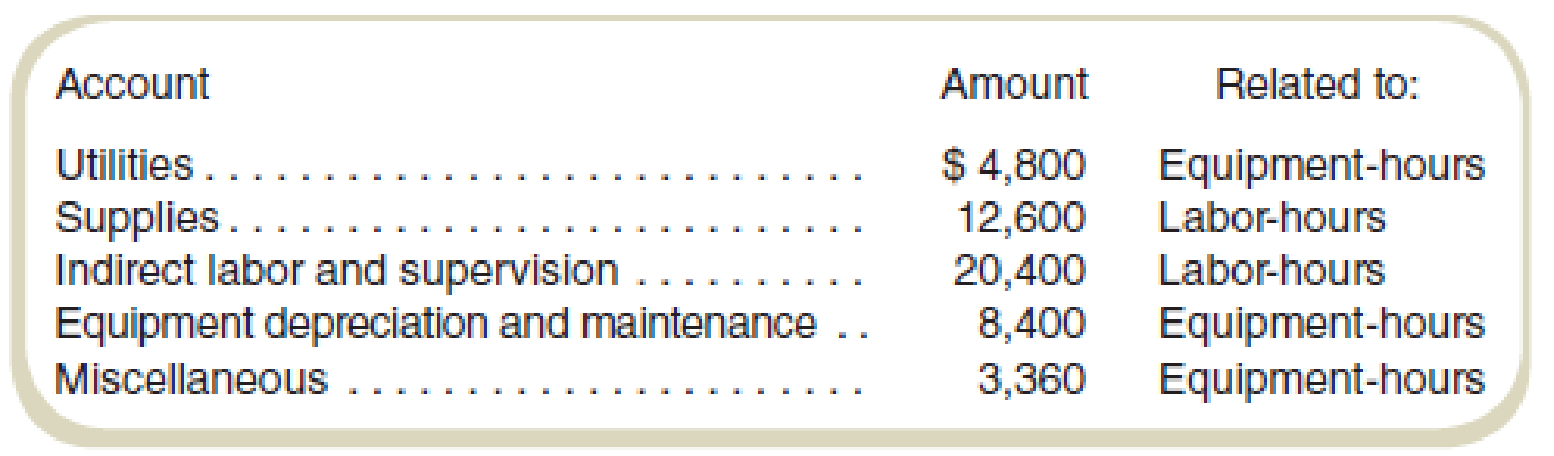
Required
- a. Compute the predetermined overhead rates assuming that Owl-Eye Radiologists uses equipment-hours to allocate equipment-related overhead costs and labor-hours to allocate labor-related overhead costs.
- b. Compute the total costs of production and the cost per unit for each of the two types of patients undergoing tests in June.
a.
Calculate the predetermined overhead rates using equipment-hours for the allocation of equipment related overhead costs and labor-hours to allocate labor-related overhead costs.
Answer to Problem 56P
The Cost per unit is $46 for the overhead rates when using equipment-hours for allocation.
The Cost per unit is $50 for the overhead rates when using labor-hours for allocation.
Explanation of Solution
Predetermined overhead rate:
The predetermined overhead rate is the rate computed for applying manufacturing overheads to the work-in-process inventory. This rate can be computed by dividing the total amount of manufacturing overheads by the base of allocation.
Analysis of overhead accounts by the cost accountant is as follows:
| Account | Amount | Related to: |
| Utilities | $ 4,800 | Equipment hours |
| Supplies | 12,600 | Labor-hours |
| Indirect labor and supervision | 20,400 | Labor-hours |
| Equipment depreciation and maintenance | 8,400 | Equipment hours |
| Miscellaneous | 3,360 | Equipment hours |
Compute equipment-hours related predetermined rate:
Hence, the equipment-hours related predetermined rate is $46.
Compute materials cost related predetermined rate:
Thus, the labor-hours related predetermined rate is $50.
b.
Compute the total costs of production and the cost per unit for each of the two types of patients undergoing tests in June.
Answer to Problem 56P
For hospital patients:
Total cost: $73,440
Cost per unit: $115
For other patients:
Total cost: $25,320
Cost per unit: $29
Explanation of Solution
Product cost:
Product cost includes all the costs that are attributed to the production of the product. All the money that has spent on the process of production or purchase of the product is known as product cost.
Product cost per unit:
The product cost per unit is determined by dividing the total of variable and fixed cost with the total number of units.
Compute the total cost of hospital patients:
Compute total cost of other patients:
Thus, the value of total cost for hospital patients and other patients are $73,440 and $25,320 respectively.
Compute cost per unit for product hospital patients:
Compute cost per unit for the product of other patients:
Working note 1:
Compute equipment hours related cost for hospital patients:
Working note 2:
Compute labor hours related cost for hospital patients:
Working note 3:
Compute equipment hours related cost for other patients:
Working note 4:
Compute labor hours related cost for other patients:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Cost Accounting (6th Edition)
- Deepa Dalal opened a free-standing radiology clinic. She had anticipated that the costs for the radiological tests would be primarily fixed, but she found that costs increased with the number of tests performed. Costs for this service over the past nine months are as follows: Required: 1. Prepare a scattergraph based on the preceding data. Use cost for the vertical axis and number of radiology tests for the horizontal axis. Based on an examination of the scattergraph, does there appear to be a linear relationship between the cost of radiology service and the number of tests? 2. Compute the cost formula for radiology services using the high-low method. 3. Calculate the predicted cost of radiology services for October for 3,500 tests using the formula found in Requirement 2.arrow_forwardProvidence Hospital generates monthly performance reports for each of its departments. The hospital must maintain an adequate staff of attending and on-call physicians at all times, so physician costs are not affected by the number of patient visits. But all other costs do vary with patient activity. Nurse- hours are used as the activity measure for nursing costs, and patient visits are used as the activity measure for the cost of supplies and other variable costs. The head physician of the hospital's emergency room, Yolanda Mortensen, is responsible for control of costs. During October, the emergency room unit expected to treat 3,500 patients but actually treated 4,000 patients. The following additional information for October is available: Budget Actual Variance Nurse-hours 2,100 2,320 -220 Nursing costs $46,200 $30,000 $16,200 Supplies & other variable $38,500 $25,500 $13,000 costs Fixed costs $104,200 $109,900 $-5,700 Required Compute the flexible-budget variances for each of the…arrow_forwardCompute the linear cost function, relating total overhead costs to physician contact hours, using the representative observations of 200 and 300 hours. Plot the linear cost function. Does the constant component of the cost function represent the fixed overhead costs of Young and Associates? Why?arrow_forward
- 1. What are the fees for a Basic Exam, Advanced Exam, and a Basic Exam assuming the goal is to cover only variable and fixed direct costs? Assume that the audiology department is allocated $100,000 in total overhead by the clinic, and the department director has allocated $50,000 of this amount to the three services listed above. (To answer this question, assume that the allocation of overhead costs to each service is made on the basis ofnumberof visits.) 2. What are the fees for a Basic Exam, an Advanced Exam, and a Basic Exam assuming the overhead costs must be covered? 7.2 The audiology department at Randall Clinic offers many services to the clinic's patients. The three most common, along with cost and utilization data, are as follows: Copying and distribution of this PDF is prohibited without written permission. For permission, please contact Copyright Clearance Center at www.copyright.com Healthcare Finance Variable Cost Annual Direct Annual Number per Service Fixed Costs of…arrow_forwardSuppose Tulsa Medical Supply Company were to use a single predetermined overhead rate based on machine hours. Compute the rate per hour. Under the approach in requirement 3, how much overhead would be assigned to the medical-testing agent order? In total. Per box of testing agent.arrow_forwardpartial list of Foothills Medical Center’s costs follows:a. Cost of laundry services for operating room personnelb. Salary of intensive care personnelc. Depreciation on patient roomsd. Cost of blood testse. Nurses’ salariesf. Cost of patient mealsg. Overtime incurred in the Patient Records Department due to a computerfailureh. Operating room supplies used on patients (catheters, sutures, etc.)i. Doctor’s feej. Cost of X-ray testk. Cost of maintaining the staff and visitors’ cafeterial. Cost of drugs used for patientsm. Cost of intravenous solutions used for patientsn. Cost of improvements on the employee parking loto. Salary of the nutritionistp. General maintenance of the hospitalq. Cost of advertising hospital services on televisionr. Cost of new heart wings. Training costs for nursest. Depreciation of X-ray equipmentu. Utility costs of the hospital Instructions1. What would be Foothills Medical Center’s most logical definition for the final cost object? Explain.2. Identify whether…arrow_forward
- What types of overhead costs are considered in job costing for hospitals, and how are they allocated to patients or procedures?A. Facility Costs - Rent, property taxes, utilities B. Administrative Costs - Salaries of administrative staff, office supplies, software systems, and legal fees C. Medical supplies and Equipment - Overhead costs also cover the expenses incurred in maintaining and replenishing medical supplies, equipment, and instruments used throughout the hospital. Can you think of any other overhead costs that may be considered when a hospital is determining the cost of a procedure?arrow_forwardBeckley Hill (BH) is a private hospital carrying out two types of procedures on patients. Each type of procedure incurs the following direct costs: Procedure A B $ 1,200 800 $ Surgical time and materials 2,640 Anaesthesia time and materials 1,620 BH currently calculates the overhead cost per procedure by taking the total overhead cost and simply dividing it by the number of procedures, then rounding the cost to the nearest 2 decimal places. Using this method, the total cost is $2,475-85 for Procedure A and $4,735-85 for Procedure B. Recently, another local hospital has implemented activity-based costing (ABC). This has led the finance director at BH to consider whether this alternative costing technique would bring any benefits to BH. He has obtained an analysis of BH's total overheads for the last year and some additional data, all of which is shown below: $ 1,870,160 6,215,616 966,976 8,553,600 Cost Cost driver Administrative costs Nursing costs Catering costs General facility costs…arrow_forward2. The administrator of ABC Hospital would like to know the relationship between the costs of admitting in relation to the number of patients being admitted and determine the cost formula. The following are the related data for the past five months that will be used determine such cost formula.Month | # of Patients Admitted |Admitting CostsJanuary 1,800 P 14,700February 1,900 P 15,200March 1,700 P 13,700April 1,600 P 14,000May 1,500 P 14,300The controller suggested to use the high-low method approach to derive for the cost formula. If the controller’s suggestion is to be followed:How much would be the total fixed costs?arrow_forward
- Poehling Medical Center has a single operating room that is used by local physicians to perform surgical procedures. The cost of using the operating room is accumul patient procedure and includes the direct materials costs (drugs and medical devices), physician surgical time, and operating room overhead. On January 1 of the current year, the annual operating room overhead is estimated to be: Disposable supplies Depreciation expense Utilities Nurse salaries Technician wages $281,800 50,800 29,600 423,200 Total operating room overhead 138,600 $924,000 The overhead costs will be assigned to procedures based on the number of surgical room hours. Poehling Medical Center expects to use the operating room an average of eight ho per day, seven days per week. In addition, the operating room will be shut down two weeks per year for general repairs. a. Calculate the estimated number of operating room hours for the year. 12 X hours b. Determine the predetermined operating room overhead rate for…arrow_forwardCrosswinds Hospital plans to use activity-based costing to assign hospital indirect costs to the care of patients. The hospital has identified the following activities and activity rates for the hospital indirect costs: Activity Activity Rate Room and meals $230 per day Radiology $185 per image Pharmacy $50 per physician order Chemistry lab $90 per test Operating room $1,030 per operating room hour The activity usage information associated with the two patients is as follows: Abel Putin Cheryl Umit Number of days 6 days 3 days Number of images 5 images 3 images Number of physician orders 7 orders 2 orders Number of tests 6 tests 2 tests Number of operating room hours 9 hours 5 hours This information has been collected in the Microsoft Excel Online file. Open the spreadsheet, perform the required analysis, and input your answers in the questions below. Open spreadsheet Determine the activity cost associated with each patient.…arrow_forward1. The administrator of ABC Hospital would like to know the relationship between the costs of admitting in relation to the number of patients being admitted and determine the cost formula. The following are the related data for the past five months that will be used determine such cost formula. Month |# of Patients Admitted |Admitting Costs January 1,800 P 14,700 February 1,900 P 15,200 March 1,700 P 13,700 April 1,600 P 14,000 May 1,500 P 14,300 The controller suggested to use the high-low method approach to derive for the cost formula. If the controller’s suggestion is to be followed: How much would be the variable cost per unit? 2. The administrator of ABC Hospital would like to know the relationship between the costs of admitting in relation to the number of patients…arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning


