
Concept explainers
a
Interpretation:
Critical path of this network.
Concept Introduction: The critical path is the arrangement of project activities which gives an estimated time duration under which the project will be completed. The project activities may include float activities which can be delayed focusing on the shortest time duration.
a
Explanation of Solution
Project network diagram for given information:
The below image shows the project network with the early start, early finish, late start and late finish:
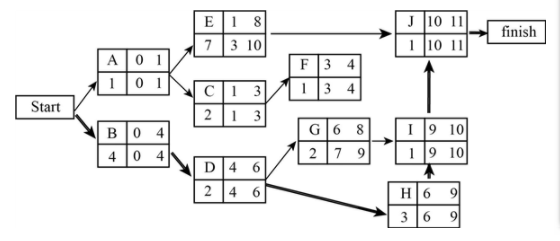
The critical path in the project network:
The paths in the given project network are as follows:
A-E-J
A-C-F
B-D-G-I-J
B-D-H-I-J
There are four paths in the project network.
Out of the above mentioned path, the path that has the equal early start and late start at the same time early finish and late finish are the critical path.
Here two paths are satisfying the above condition, which are as follows:
A-C-F
B-D-H-I-J
When the network has more than one critical path, the path, which has the maximum project completion time, should be selected.
Hence, the critical path is B-D-H-I-J.
b
Interpretation:
Completion time of the project.
Concept Introduction: Early start time: The rule for the early start time of a task is that it is equal to the largest early finish time of the task’s immediate predecessors.
Early finish time: The early finish time of a task is the addition of both task time and early start time of the task.
b
Explanation of Solution
When the network has more than one critical path, the path, which has the maximum project completion time, should be selected.
A-C-F
B-D-H-I-J
Hence, the critical path is B-D-H-I-J.
As the critical path is determined as B-D-H-I-J, the project completion time is 11 days.
c
Interpretation:
The slack of activity A.
Concept Introduction: The critical path is the arrangement of project activities which gives an estimated time duration under which the project will be completed. The project activities may include float activities which can be delayed focusing on the shortest time duration.
c
Explanation of Solution
The slack of the activity is calculated by subtracting the early start from the late finish.
Hence, the slack of activity A is 0.
d
Interpretation:
Task to be crashed and its cost.
Concept Introduction: The critical path is the arrangement of project activities which gives an estimated time duration under which the project will be completed. The project activities may include float activities which can be delayed focusing on the shortest time duration.
d
Explanation of Solution
The cost of crashing.
It is given that the paths should be crashed and the total time of the path should not exceed 8 days. The cost to crash Activity B is $500 per crash, Activity H is $200 per crash, and all eligible activities are $100 per crash.
Use the following steps to crash the activities:
The paths and the total task time to complete the path within 8 days is shown below:
Path A-E-J:
Total task time is calculated by adding the duration of all the activities in the path.
Hence, the total task time is 9 days. It exceeds 8 days. Thus, the path should be crashed. Activity A and Activity J cannot be crashed as the duration is 1. Activity E should be crashed from 7 days to 6 days.
Hence, the total task time is 4 days. It does not exceed 8 days. Thus, the path cannot be crashed.
Path B-D-G-I-J:
Total task time is calculated by adding the duration of all activities in the path.
Hence, the total task time is 10 days. It exceeds 8 days. Thus, the path should be crashed. However, it costs $500 to crash one day of Activity B. Thus, Activity D and Activity G can be crashed from 2 days to 1 day.
The cost for crashing is $200 as the crashing was done for two days in Activity D and Activity G. It is given that the activities except for Activity B and H cost $100 per day.
Path B-D-H-I-J
Total task time is calculated by adding the duration of all the activities in the path.
Hence, the total task time is 10 days. It exceeds 8 days. Thus, the path should be crashed. Activity I, Activity D (crashed in the previous step), Activity J cannot be crashed as the duration is 1 day. Activity B can be crashed. However, it costs $500 to crash one day of Activity B. Thus, Activity H can be crashed from 3 days to 2 days.
The cost for crashing is $400 as the crashing was done for two days in Activity H. It is given Activity H costs $100 per day.
Total crashing cost:
Total crashing cost is calculated by adding all the crashing cost done in the previous steps.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Practical Operations Management
- A project has the activity duration and cost information indicated in the table where all times are in weeks. What is the total cost for completing this project in 50 days? Activity Predecessor Normal Time Normal Cost Crash Time Crash Cost A -- 8 $12,000 5 $21,000 B A 12 $20,000 9 $30,000 C A 15 $24,000 10 $60,000 D B 3 $10,000 2 $15,000 E C 9 $17,000 6 $34,000 F E 7 $5,000 6 $6,000 G D 8 $14,000 6 $20,000 H A 12 $22,000 10 $30,000 I H 6 $50,000 5 $55,000 J F, G, I 11 $33,000 9 $50,000arrow_forwardUsing the information provided in the table, the network diagram and the project completion time = 25 weeks, reduce the completion time of the project by 3 weeks in the most economical way. Activity NormalTime(weeks) NormalCost ($) CrashTime(weeks) CrashCost ($) MaximumweeksReduced CrashCost perWeek ($) A 3 500 2 900 1 400 B 4 600 3 700 1 100 C 6 800 3 1,286 3 162.00 D 6 1,500 4 2,150 2 325 E 6 1,750 4 2,250 2 250 F 5 1,200 5 1,200 0 0 G 7 1,500 5 1,794 2 147 H 3 500 3 500 0 0 Reduce G by select a number of (1-4) week(s), C by select a number (1-4) of week(s), at a cost of $ __________ enter a dollar amount .arrow_forwardWe are planning to develop a room reservation system that is estimated to have 400 story points of features. Let’s say our team’s velocity on two-week sprints ranges between 20 and 25 story points. Our project will start on Dec 1, 2021. If our customer wants the project to be in production by end of June 22, how likely will the project be successful? Why? Show your calculations.arrow_forward
- Development of Version 2.0 of a particular accounting software product is being considered by Jose Noguera's technology firm in Baton Rouge. The activities necessary for the completion of this project are listed in the following table: Activity Normal Time(weeks) Crash Time(weeks) Normal Cost Total Cost with Crashing Immediate Predecessor(s) A 4 3 $2,000 $2,650 — B 2 1 $2,100 $2,900 — C 3 3 $750 $750 — D 8 4 $2,300 $2,620 A E 6 3 $900 $1,275 B F 3 2 $3,200 $4,700 C G 4 2 $1,400 $1,900 D, E I have answers for the frist part of the question: a) Based on the given information regarding the activities for the project, the project length = 16 weeks. b) The total cost required for completing this project on normal time = $12,650. c) For reducing the duration of the project by one week, the activity that should be crashed first is activity…arrow_forwardDevelopment of Version 2.0 of a particular accounting software product is being considered by Jose Noguera's technology firm in Baton Rouge. The activities necessary for the completion of this project are listed in the following table: Activity Normal Time(weeks) Crash Time(weeks) Normal Cost Total Cost with Crashing Immediate Predecessor(s) A 4 3 $2,000 $2,650 — B 2 1 $2,100 $2,900 — C 3 3 $750 $750 — D 8 4 $2,300 $2,620 A E 6 3 $900 $1,275 B F 3 2 $3,200 $4,700 C G 4 2 $1,400 $1,900 D, E a) Based on the given information regarding the activities for the project, the project length = 16 weeks. b) The total cost required for completing this project on normal time = $12,650. c) For reducing the duration of the project by one…arrow_forwardManagement & Science University (MSU) have appointed you as a project manager to conduct a Joint Application Design (JAD) session with members from various departments. As a project manager, you are required to develop a specific schedule for the tasks listed below. The estimated task duration for each shown in parentheses. First, you must contact and brief the participants and explain their responsibilities (1 day). Then you must obtain approval from their department managers (3 days). After you have obtained the approval, you can begin the two tasks where you can prepare the agenda for the JAD session (7 days) and arrange the meeting room (2 days) When the agenda is ready, you can start two more concurrent tasks which are preparing the information packets (4 days) and to create visual aids (8 days). When the meeting room is arranged and information packets are ready, you can send out an email to all participants (1 day). Finally, after the e-mail is sent to participants and the…arrow_forward
- Project B is the development of a facility in a remote area, of about GHS 5 million in value, of approximately 18 months’ planned duration. It is 30 per cent completed. Earned Value analysis shows that the project is not achieving its planned cost or progress targets. The project is also not achieving quality requirements. Some of the specialized components used for this project are only obtainable from overseas suppliers and are difficult to transport over the rough terrain near the project site. There has been a delay on ordering these components. The transportation of these components, which must be booked several months ahead, has not been arranged, and there is also difficulty with obtaining tradespeople with the requisite set of skills to install them. There are also several other risks associated with this project, including a quite basic business case, rudimentary project charter, poor definition of expected project outcomes, exchange rate risks and the potential for…arrow_forwardTwo critical path activities are candidates for crashing on a CPM network. Activity details are in the table below. To cut two days from the project's duration, to project cost and activity should be crashed second, adding to project cost. activity should be crashed first, adding Activity Normal Time Normal Cost Crash Time Crash Cost 8 days $6,000 7 days $6,400 10 days $4,000 9 days $5,000 B A; $400 and then A; $400 nA; $400 and then B; $1000 n B; $1000 and then A; $400 B; $1000 and then B; $1000arrow_forwardIn reference to the attached image and data below: Step A we learned: Critical Path = A, B, H, I, J; Project Time = 40 Weeks; Total Cost = 364,000 Step B we learned: To crash the critical path I would crash A by 1 week, B by 2 week, H by 2 week and C by 3 week. This would not alter the critical path, only the time line. Steps C we learned: Modeling uncertainty in activity times. In this case I would use the activity times and determine the Variances and the Standard Deviation. Using “best case” (x) and “worst case” (y) scenarios for activity times the formula’s would be (x-y)/6 and (x-y)^2/36. What are the final recommendations for this case?arrow_forward
- General Foundry’s project crashing data are shown below. Crash this project to 13 weeks using CPM. What is the final time for each activity after crashing? What is the crash cost per week per activity and the total cost of crashing? TIME (WEEKS) COST ($) ACTIVITY IMMEDIATE PREDECESSORS NORMAL CRASH NORMAL CRASH A — 2 1 22,000 23,000 B — 3 1 30,000 34,000 C A 2 1 26,000 27,000 D B 3 2 48,000 49,000 E C 4 2 56,000 58,000 F C 3 2 30,000 30,500 G D, E 5 2 80,000 83,000 H F, G 2 1 16,000 19,000arrow_forwardConsider a project that has been modeled as in the table below. Part a) Draw the PERT/CPM network for this project and determine the project’s expected completion time μP and its critical path. Part b) Suppose the standard deviations of the activity durations are σA = 2, σB = 1, σC = 0, σD = 2, σE = 3, and σF = 0. Then please estimate the standard deviation of the overall project’s standard deviation σP . Part c) Suppose for the standard Normal random variable Z, we know P[−1 ≤ Z ≤ +1] ' 68%, P[−2 ≤ Z ≤ +2] ' 95%, and P[−3 ≤ Z ≤ +3] ' 99.7%. Then, approximately what time T is one for which there is only a less than 2.5% chance for the completion time to beat (be shorter than)? *Please answer a-c and type your work and answers or write them neatly please* Thank youarrow_forwardDraw a network diagram showing the linkage between these activities from start to finish. For the diagram, each activity should be labelled alphabetically ie. A, B, C… etc. PERT Formula: TE = (O + 4T + P) / 6 TE = Pert Expected Time Duration, O = Optimistic estimate, P = Pessimistic estimate, T = Most Likely (Typical) estimate Activity Predecessor Optimistic Most Likely Pessimistic Duration Duration in Weeks A — 2 3 4 B — 4 5 7 C B 1 2 3 D C & E 0.5 1 1.5 E B 0.5 1 1.5 F C 2 3 4 G F 2 3 4arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.





