
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The structure of the compound with molecular formula
Concept introduction:
Mass spectrometry is a technique used for measuring the masses of atoms and molecules with great accuracy.
In a mass spectrometer, the vapor of organic compound is bombarded with a beam of high energy electrons that makes the neutral molecule lose an electron and converts it to a radical cation known as a molecular ion.
In
In
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is one of the most capable analytical techniques used for determining the
Few elements, such as
In
Induced magnetic field consists of electricity generated from movement in a magnetic field.
The position of a signal on x-axis in the
The number of signals in
The area covered by the signal is proportional to the number of equivalent protons causing the signal.
The hydrogen atoms on adjacent carbon atoms split the signal into two or more peaks. One, two or three hydrogen atoms split the signal into two, three or four peaks described as doublet, triplet or quartet respectively.
A decrease in the electron density around a proton deshields the signal downfield at a larger value of chemical shift.
An increase in electron density shields the signal upfield at a lower value of chemical shift.
The peak at
The peak at
The peak at
Answer to Problem 1PP
Solution: The structure of the compound with molecular formula
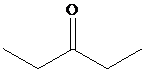
Explanation of Solution
The figure given below represents the
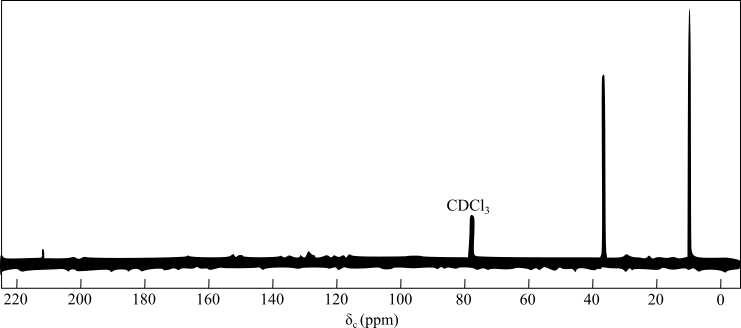
In DEPT
The peak at
The peak at
The peak at
The presence of two signals in the alkyl group region indicates the presence of symmetry in the compound and the two unique carbon atoms.
Therefore, the structure of the compound is as:

The structure of the compound with molecular formula

Want to see more full solutions like this?
- 1- The number of the signals for the following compound in DEPT-90 experiment will be: (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4arrow_forward05 Question See page 749 If a compound contains 14 carbons (for example, C₁4H30) and the M+ peak is the base peak, what relative intensity would you expect for the M +1 peak? 4th attempt Enter the relative intensity with one decimal place.. % See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardPart E Approximate chemical shift for groups a, b, and c (note the order in the image). a H На b c -OCH,CH3 b CH;CH,O- a H На O 2.3, 0.9, 2.3 O 2.3, 3-4, 0.9 O 7.2, 3-4, 2.3 O 7.2, 3-4, 0.9 Submit Request Answer Part F What are the splitting values for groups a, b, and c (note the order in the image). a H На b c OCH,CH3 с b CH;CH,O- a H На O singlet, quartet, triplet doublet, triplet, quartet O singlet, doublet, triplet O singlet, triplet, doublet Submit Request Answerarrow_forward
- Which of the following IR frequencies would be expected for ethanol? Select all that apply. ~1710 cm¹ (broad) ~2870 cm 1 O~2250 cm 1 0-3075 cm ¹ ~3410 cm1 (broad)arrow_forwardGiven the following spectrum, estimate Amax: 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 380 430 480 530 580 Wavelength (nm) Trouble viewing? a) 390 nm b) 410 nm c) 430 nm d) 550 nm Absorbancearrow_forwardH NMR (300 mMHz, CDCl3, 21C) 0.92 ppm (t, 3H, J = 7Hz), 1.20 (s, 6H), 1.50 (q, 2H, J = 7 Hz), 1.64 (broad singlet, 1H). Choose the chemical shift of the three lines in the triplet signal at 0.92 ppm? (Select all correct answers) a b с d f b0 0.920 ppm 0.897 ppm 0.943 ppm 7.920 ppm 6.080 ppm 0.998 ppm 0.842 ppmarrow_forward
- Correct Answer How many signals would you expect to find in the HNMR spectrum of this compound? a) 2 b) 3 ⠀ c) 4 á d) 5 e) 6 You Answered Correct! Question 7 DA OD Question 4 How many signals would you expect to find in the HNMR spectrum of the following compound? (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 5 D E C D хаarrow_forwardneed help ASAP, thanks Which of the following structures would be expected to show the parent molecular ion peak of [M] = 98 m/z (select all that apply)?arrow_forwardProton NMR Example 4: Predict The Spectrum H3C-0 H3C d CIarrow_forward
- D Question 5 For a 2D spectrum with 5 peaks on the diagonal, how many off- diagonal peaks are expected а. 1 O b. 2 с. 3 d. 4arrow_forwardQ: Determine the structure of the following unknowns using the table to fill in your answers. B C B Signal 8 Integration Multiplicity Comments A C S J D C₂H₁0O₂ E 3 C10H120 PPM Signal & Integration Multiplicity Comments A 3 DOM Larrow_forwardHello, Please find the M peak, M+1 peak, and M+2 peak. Thank you.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
