
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The electrophilic group for the given reaction is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one
Answer to Problem 5.1P
In the given reaction, iodine cation is behaving as an electrophile.
Explanation of Solution
In acid catalyzed hydration reaction, nucleophile goes to the more substituted carbon of the
In the given reaction, addition of electrophile over carbon-carbon double bond takes place. This will result in the formation of intermediate that is carbocation. Thus, the addition of electrophile is at less substituted carbon of the alkene to give the desired product as shown below.
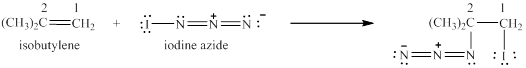
Figure 1
In this case, azide ion is behaving as a nucleophile, whereas iodine cation is behaving as an electrophile.
In the given reaction, iodine cation is behaving as an electrophile.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed by the given reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons are known as a nucleophile. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving group by attacking the electron deficient carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 5.1P
The product formed by the given reaction is shown below.
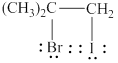
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is,
![]()
Figure 2
The electronegativity of bromine is higher than iodine, thus due to which in iodine bromide iodine will act as an electrophile, whereas bromide ion will act as a nucleophile. The given reaction will follow Markovnikov’s rule to form the desired product as shown below.

Figure 3
The product formed by the given reaction is shown in Figure 3.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- When aniline, C6H5NH2(Kb=7.41010) , reacts with a strong acid, its conjugate acid, C6H5NH3+, is formed. Calculate the pH of a 0.100 M solution of C6H5NH3+ and compare it with the pH of acetic acid (Ka=1.86105) .arrow_forwardWhen the conjugate acid of aniline, C6H5NH3+, reacts with the acetate ion, the following reaction takes place: C6H5NH3+(aq)+CH3COO(aq)C6H5NH2(aq)+CH3COOH(aq) If Kafor C6H5NH3+ is 1.35105 and Kafor CH3COOH is 1.86105 , what is K for the reaction?arrow_forward5. Give the structural formulae and name the functional groups of the following compounds. (a) 3-chlorobut-1-ene (b) butanedioic acid Name the functional group: (c) propanamide Name the functional group: (d) 3-methylbutanal Name the functional group: Name the functional group:arrow_forward
- Draw the structures of the following compounds:(a) Ethanoic acid(b) Bromopentane(c) Butanonearrow_forwardBiphenyl has the following structure.(a) Is biphenyl a (fused) polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon?(b) How many pi electrons are there in the two aromatic rings of biphenyl? How does this number compare with that for naphthalene?(c) The heat of hydrogenation for biphenyl is about 418 kJ>mol (100 kcal>mol). Calculate theresonance energy of biphenyl.(d) Compare the resonance energy of biphenyl with that of naphthalene and with that of two benzene rings. Explain thedifference in the resonance energies of naphthalene and biphenyl.arrow_forwardGive the structural formulae and name the functional groups of the following compounds. (a) 3-chlorobut-1-ene Name the functional group: (b) butanedioic acid Name the functional group: (c) propanamide Name the functional group: (d) 3-methylbutanal Name the functional group:arrow_forward
- (a) Write a chemical test to distinguish between: (i) Chlorobenzene and Benzyl chloride. (ii) Chloroform and Carbon tetrachloride. (b) Why is methyl chloride hydrolysed more easily than chlorobenzene?arrow_forwardIdentify which of the following statement(s) is/are true. (f) Aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters all contain a carbonyl group. (g) A compound with the molecular formula of C3H6O may be either an aldehyde, a ketone, or a carboxylic acid. (h) Bond angles about the carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde, a ketone, a carboxylic acid, and an ester are all approximately 109.5°. (i) The molecular formula of the smallest aldehyde is C3H6O, and that of the smallest ketone is also C3H6O. (j) The molecular formula of the smallest carboxylic acid is C2H4O2.arrow_forwardPhotochemical chlorination of 2,2,4-trimethylpentane gives four isomeric monochlorides. (a) Write structural formulas for these four isomers. (b) The two primary chlorides make up 65% of the monochloride fraction. Assuming that all the primary hydrogens in 2,2,4-trimethylpentane are equally reactive, estimate the percentage of each of the two primary chlorides in the product mixture.arrow_forward
- 5.Write the structural formula of the ester that, when hydrolyzed, would yield the following:(a) methanol and propanoic acid(b) 1-octanol and acetic acid (c) ethanol and butanoic acidarrow_forwardExplain why an amide ion cannot be used to form a carbanion from an alkane in a reaction that favors products.arrow_forwardEster formation and ester hydrolysis are exactly the same reaction only written in reverse. General reaction of ester formation: H*, heat R—с—он + Н—о—R' R—с—о-R' + H,O carboxylic acid alcohol carboxylic or phenol ester General reaction of ester hydrolysis: || R—с—OR' + H—оН R—с—оН +R—ОH ester carboxylic acid alcohol or phenol What determines which direction the reaction proceeds and what actually forms? o the boiling point of the carboxylic acid o the presence (or absence) of heat as well as the concentration of reactants and products o the molecular weight of reactants and products o the presence (or absence) of heat as well as the catalystarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
